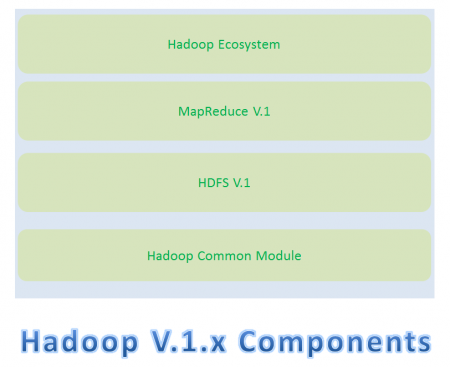
Hadoop V.1.x Components
Apache Hadoop V.1.x has the following two major Components
- HDFS (HDFS V1)
- MapReduce (MR V1)
In Hadoop V.1.x, these two are also know as Two Pillars of Hadoop.
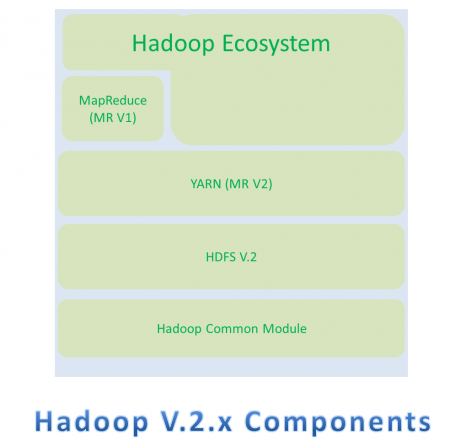
Hadoop V.2.x Components
Apache Hadoop V.2.x has the following three major Components
- HDFS V.2
- YARN (MR V2)
- MapReduce (MR V1)
In Hadoop V.2.x, these two are also know as Three Pillars of Hadoop.
Hadoop 1.x has the following Limitations/Drawbacks:
For Example:- Suppose, 10 Map and 10 Reduce Jobs are running with 10 + 10 Slots to perform a computation. All Map Jobs are doing their tasks but all Reduce jobs are idle. We cannot use these Idle jobs for other purpose.
- It is only suitable for Batch Processing of Huge amount of Data, which is already in Hadoop System.
- It is not suitable for Real-time Data Processing.
- It is not suitable for Data Streaming.
- It supports upto 4000 Nodes per Cluster.
- It has a single component : JobTracker to perform many activities like Resource Management, Job Scheduling, Job Monitoring, Re-scheduling Jobs etc.
- JobTracker is the single point of failure.
- It does not support Multi-tenancy Support.
- It supports only one Name Node and One Namespace per Cluster.
- It does not support Horizontal Scalability.
- It runs only Map/Reduce jobs.
- It follows Slots concept in HDFS to allocate Resources (Memory, RAM, CPU). It has static Map and Reduce Slots. That means once it assigns resources to Map/Reduce jobs, it cannot re-use them even though some slots are idle.
Differences between Hadoop 1.x and Hadoop 2.x
If we observe the components of Hadoop 1.x and 2.x, Hadoop 2.x Architecture has one extra and new component that is : YARN (Yet Another Resource Negotiator).
It is the game changing component for BigData Hadoop System.
As shown in the below diagram, Hadoop 1.x is re-architected and introduced new component to solve Hadoop 1.x Limitations.
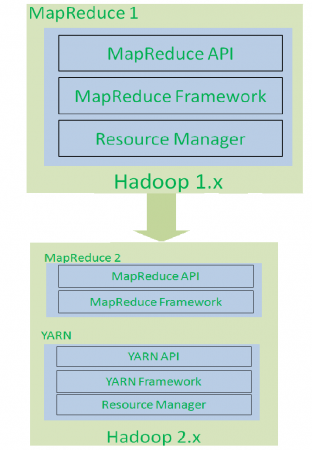
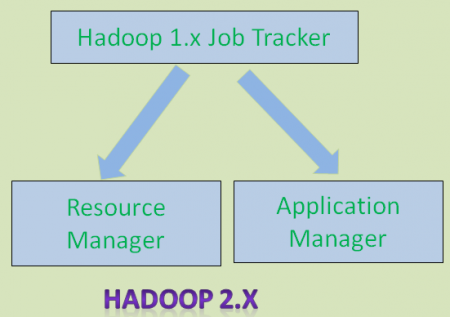
As shown in the below diagram, Hadoop 1.x Job Tracker component is divided into two components:
To manage resources in cluster
To manage applications like MapReduce, Spark etc.
- Hadoop 1.x supports only one namespace for managing HDFS filesystem whereas Hadoop 2.x supports multiple namespaces.
- Hadoop 1.x supports one and only one programming model: MapReduce. Hadoop 2.x supports multiple programming models with YARN Component like MapReduce, Interative, Streaming, Graph, Spark, Storm etc.
- Hadoop 1.x has lot of limitations in Scalability. Hadoop 2.x has overcome that limitation with new architecture.
- Hadoop 2.x has Multi-tenancy Support, but Hadoop 1.x doesn’t.
- Hadoop 1.x HDFS uses fixed-size Slots mechanism for storage purpose whereas Hadoop 2.x uses variable-sized Containers.
- Hadoop 1.x supports maximum 4,000 nodes per cluster where Hadoop 2.x supports more than 10,000 nodes per cluster.
How Hadoop 2.x solves Hadoop 1.x Limitations
Hadoop 2.x has resolved most of the Hadoop 1.x limitations by using new architecture.
- By decoupling MapReduce component responsibilities into different components.
- By Introducing new YARN component for Resource management.
- By decoupling component’s responsibilities, it supports multiple namespace, Multi-tenancy, Higher Availability and Higher Scalability.
Hadoop 2.x YARN Benefits
Hadoop 2.x YARN has the following benefits.
- Highly Scalability
- Highly Availability
- Supports Multiple Programming Models
- Supports Multi-Tenancy
- Supports Multiple Namespaces
- Improved Cluster Utilization
- Supports Horizontal Scalability
That’s it all about Differences between Hadoop 1.x and Hadoop 2.x.
 REGISTER FOR FREE WEBINAR
X
REGISTER FOR FREE WEBINAR
X
 Thank you for registering
Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month
JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering
Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month
JOIN MEETUP GROUP