Advanced DevOps Certification Training with G ...
- 20k Enrolled Learners
- Weekend
- Live Class
We all know how important Containers have become in today’s fast-moving IT world. Pretty much every big organization has moved out of its traditional approach of using virtual machines and started using Containers for deployment. So, it’s high time you understand what is Kubernetes. Following are the topics covered in this blog:
If you want to read more about the advantages of Containers and how companies are reshaping their deployment architecture with Docker, click here. Or else continue reading this blog about Kubernetes.
This Edureka Kubernetes Full Course video will help you understand and learn the fundamentals of Kubernetes. This Kubernetes Tutorial is ideal for both beginners as well as professionals who want to master the fundamentals of Kubernetes.
Kubernetes is an open-source container management (orchestration) tool. Its container management responsibilities include container deployment, scaling & descaling of containers & container load balancing.
Note: Kubernetes is not a containerization platform. It is a multi-container management solution.
Going by the definition, you might feel Kubernetes is very ordinary and unimportant. But trust me, this world needs Kubernetes to manage containers as much as it needs Docker to create them. Let me tell you why! If you favor a video explanation on the same, you can go through the video below.
Companies out there may be using Docker, Rocket, or simply Linux containers to containerize their applications. But, whatever it is, they use it on a massive scale. They don’t stop at using 1 or 2 containers in Prod. But rather, 10’s or 100’s of containers for load balancing the traffic and ensuring high availability.
Keep in mind that, as the traffic increases, they even have to scale up the number of containers to service the ‘n’ no of requests that come in every second. And they have also to scale down the containers when the demand is less. Can all this be done natively?

That is why the need for container management tools is imminent. Both Docker Swarm and Kubernetes are popular tools for Container management and orchestration. But, Kubernetes is the undisputed market leader. Partly because it is Google’s brainchild and partly because of its better functionality.
Logically speaking, Docker Swarm is a better option because it runs right on top of Docker, right? If I were you, I would have had the same doubt, and it would have been my #1 mystery to solve. So, if you thinking the same, read this blog on the comparison between Kubernetes vs Docker Swarm.
If I could choose between the two, it would have to be Kubernetes. The reason simply is the Auto-scaling of containers based on traffic needs. However, Docker Swarm is not intelligent enough to do Auto-scaling. Be as it may, let’s move on to the next topic: what is Kubernetes blog?
This is the right time to talk about Kubernetes’ features because you already know what it does and how it compares against Docker Swarm.
Kubernetes Features – What Is Kubernetes
 Kubernetes automatically packages your application and schedules the containers based on their requirements and available resources while not sacrificing availability. To ensure complete utilization and save unused resources, Kubernetes balances between critical and best-effort workloads.
Kubernetes automatically packages your application and schedules the containers based on their requirements and available resources while not sacrificing availability. To ensure complete utilization and save unused resources, Kubernetes balances between critical and best-effort workloads.
 With Kubernetes, there is no need to worry about networking and communication because Kubernetes will automatically assign IP addresses to containers and a single DNS name for a set of containers, that can load-balance traffic inside the cluster.
With Kubernetes, there is no need to worry about networking and communication because Kubernetes will automatically assign IP addresses to containers and a single DNS name for a set of containers, that can load-balance traffic inside the cluster.
 With Kubernetes, you can mount the storage system of your choice. You can either opt for local storage, or choose a public cloud provider such as GCP or AWS, or perhaps use a shared network storage system such as NFS, iSCSI, etc.
With Kubernetes, you can mount the storage system of your choice. You can either opt for local storage, or choose a public cloud provider such as GCP or AWS, or perhaps use a shared network storage system such as NFS, iSCSI, etc.
 Personally, this is my favorite feature. Kubernetes can automatically restart containers that fail during execution and kills those containers that don’t respond to user-defined health checks. But if nodes itself die, then it replaces and reschedules those failed containers on other available nodes.
Personally, this is my favorite feature. Kubernetes can automatically restart containers that fail during execution and kills those containers that don’t respond to user-defined health checks. But if nodes itself die, then it replaces and reschedules those failed containers on other available nodes.
 Kubernetes can help you deploy and update secrets and application configuration without rebuilding your image and without exposing secrets in your stack configuration.
Kubernetes can help you deploy and update secrets and application configuration without rebuilding your image and without exposing secrets in your stack configuration.
 In addition to managing services, Kubernetes can also manage your batch and CI workloads, thus replacing containers that fail, if desired.
In addition to managing services, Kubernetes can also manage your batch and CI workloads, thus replacing containers that fail, if desired.
 Kubernetes needs only 1 command to scale up the containers, or to scale them down when using the CLI. Else, scaling can also be done via the Dashboard (kubernetes UI).
Kubernetes needs only 1 command to scale up the containers, or to scale them down when using the CLI. Else, scaling can also be done via the Dashboard (kubernetes UI).
 Kubernetes progressively rolls out changes and updates to your application or its configuration, by ensuring that not all instances are worked at the same instance. Even if something goes wrong, Kubernetes will rollback the change for you.
Kubernetes progressively rolls out changes and updates to your application or its configuration, by ensuring that not all instances are worked at the same instance. Even if something goes wrong, Kubernetes will rollback the change for you.
These were some of the notable features of Kubernetes. Let me delve into the attractive aspects of Kubernetes with a real-life implementation of it and how it solved a major industry worry.
I’m pretty sure everyone reading this blog would have played this famous smartphone game. Or atleast you would have heard of this game. I’m so sure because this game literally smashed every record set by gaming applications in both the Android and iOS markets.
Pokemon Go developed by Niantic Labs and was initially launched only in North America, Australia & New Zealand. In just a few weeks upon its worldwide release, the game reached 500+ million downloads with an average of 20+ million daily active users. These stats bettered, those set by games like Candy Crush and Clash of Clans.
The app backend was written in Java combined with libGDX. The program was hosted on a Java cloud with Google Cloud Bigtable NoSQL database. And this architecture was built on top of Kubernetes, making it their scaling strategy.
Rapid iteration of pushing updates worldwide was done thanks to MapReduce and in particular Cloud Dataflow for combining data, doing efficient MapReduce shuffles, and for scaling their infrastructure.
The actual challenge: For most big applications like this is horizontal scaling. Horizontal scaling is when you are scaling up your servers for servicing the increasing the number of requests from multiple players and playing environments. But for this game in particular, vertical scaling was also a major challenge because of the changing environment of players in real-time. And this change also has to be reflected to all the others playing nearby because reflecting the same gaming world to everyone is how the game works. Each individual server’s performance and specs also had to be scaled simultaneously, and this was the ultimate challenge which needed to be taken care of by Kubrenetes.
Conclusion: Not only did Kubernetes help in horizontal and vertical scaling of containers, but it excelled in terms of engineering expectations. They planned their deployment for a basic estimate and the severs were ready for a maximum of 5x traffic. However, the game’s popularity rose so much that, they had to scale up to 50x times. Ask engineers from other companies, and 95% of them will respond with their server meltdown stories and how their business went down crashing. But not at Niantic Labs, the developers of Pokemon Go.
Edward Wu, Director of Software Engineering, at Niantics said,
Pokemon Go surpassed all engineering expectations by 50x times and has managed to keep running despite its early launch problems. This became an inspiration and a benchmark for modern day augmented reality games as it inspired users to walk over 5.4 billion miles in a year. The implementation at Niantic Labs, thus made this the largest Kubernetes ever deployed.
So, now on moving onto the next part of this ‘what is Kubernetes’ blog, let me explain the working architecture of Kubernetes.
Since Kubernetes implements a cluster computing background, everything works from inside a Kubernetes Cluster. This cluster is hosted by one node acting as the ‘master’ of the cluster, and other nodes as ‘nodes’ which do the actual ‘containerization‘. Below is a diagram showing the same.
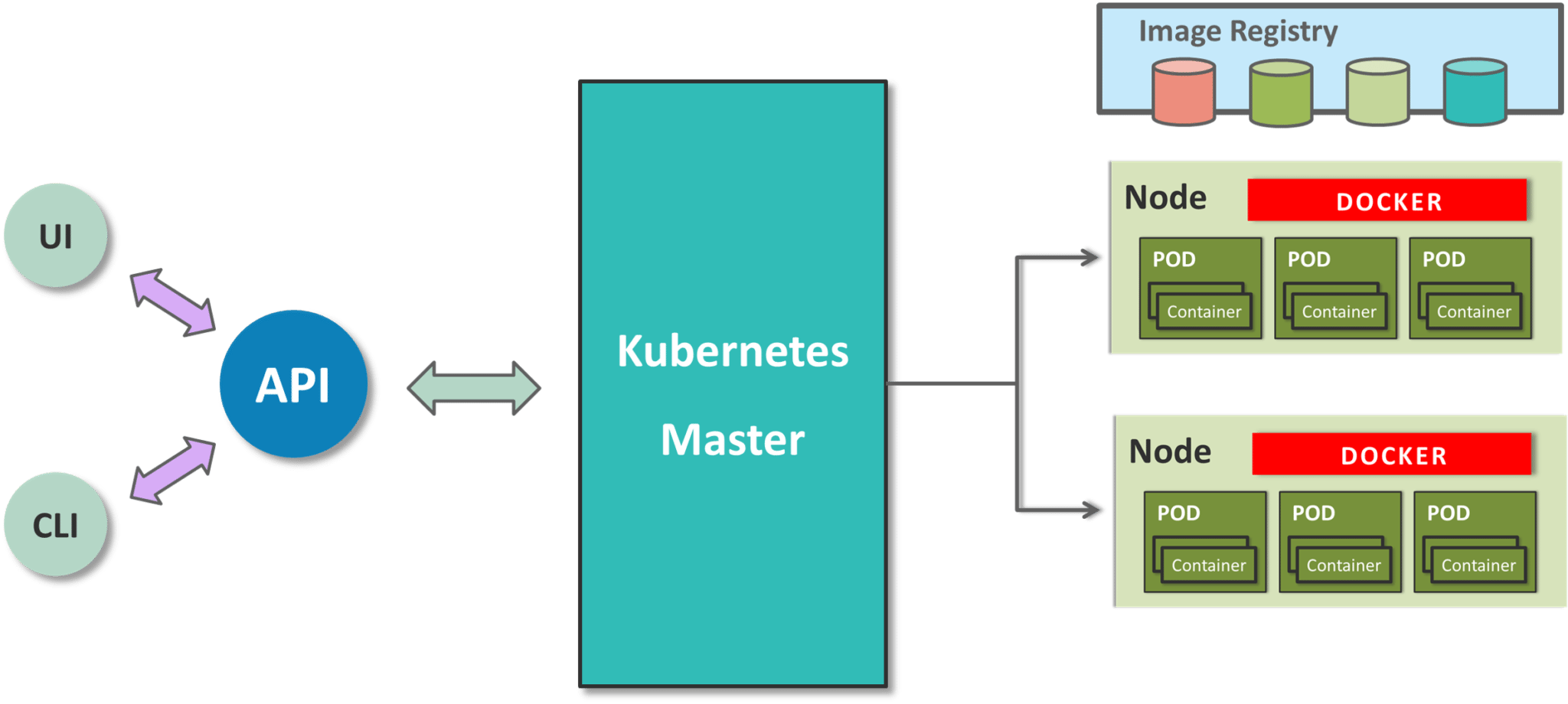
Kubernetes Architecture – What Is Kubernetes
Master controls the cluster and the nodes in it. It ensures the execution only happens in nodes and coordinates the act. Nodes host the containers; in fact these Containers are grouped logically to form Pods. Each node can run multiple such Pods, a group of containers interacting with each other, for a deployment.
The replication Controller is the Master’s resource to ensure that the requested no. of pods are always running on nodes. Service is an object on Master that provides load balancing across a replicated group of Pods.
If you want to get certified in Kubernetes, and master this tool, you can uplift your career as a DevOps Engineer with the Docker and Kubernetes training.
Got a question for us? Please mention it in the comments section of ”Kubernetes Tutorial,” I will get back to you.
So, that simply’s the Kubernetes architecture. You can expect more details on the architecture in my next blog. A better news is, the next blog will also have a hands-on demonstration of installing the Kubernetes cluster and deploying an application.
 Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUPedureka.co