PMP Certification Training
- 88k Enrolled Learners
- Weekend/Weekday
- Live Class
In layman’s term, Six Sigma is a measure of quality that strives for near perfection. The official definition for Six Sigma is: It is a disciplined, data-driven approach and methodology for eliminating defects in any process, from manufacturing to transactional and from product to service.
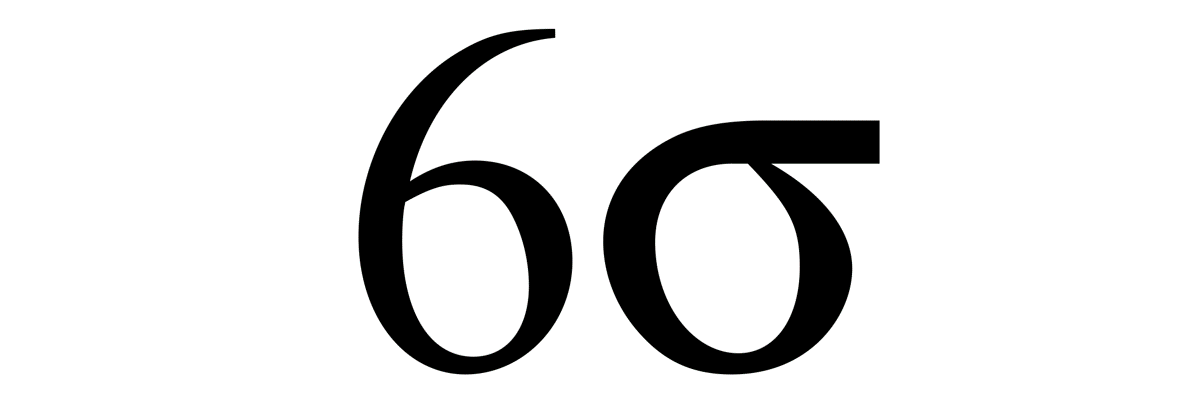
Top Organizations benefiting from Six Sigma
The fundamental objective of the Six Sigma methodology is the implementation of a measurement-based strategy that focuses on process improvement and variation reduction.
The term ‘sigma’, denoted by Greek letter σ, is used to designate the distribution or spread about the mean(average) of any process or procedure. A six sigma process is one in which 99.99966% of all opportunities to produce some feature of a part are statistically expected to be free of defects (3.4 defective features / million opportunities).
Six Sigma goes beyond defect reduction to emphasize business improvement in general, which includes:
And any other metric that is important to the company.
In the mid-1980’s Motorola, Bill Smith and Mikel Harry designed an in-house model ‘Six Sigma’ for reducing defects. The then Chairman of Motorola, Bob Galvin implemented it across all sub functions. In 1991, Allied Signal adopted Six Sigma methods followed by General Electric’s CEO Jack Welch, in 1995. By 2000, Six Sigma was effectively established and implemented in all sorts of organizations around the world. Today, around 129 organizations across the globe apply Six Sigma methodology.
According to Jack Welch, former CEO of GE, “Six Sigma is the best training that an organization can give to its employees, it’s even better than sending them to Harvard Business School.”
Business Problem:
The Business Problem is defined at the beginning of a Six Sigma project. Questions such as What, When and Where are addressed in a problem statement. The magnitude and consequence of the problem is also discussed and the Project Scope is identified at this point of time.
Statistical Problem:
At this stage, the root causes for the Business Problems are identified. The root causes are then converted into Statistical Problems using Hypothesis testing methods. The causes are of two types: Trivial Many and Vital Few.
Statistical Solution:
Identification of only 3-4 vital root causes is done using Statistical Analysis. These root causes play a vital part as they are deemed to present maximum impact on the problem. Any given problem follows a Pareto principle, where 80% of the problems are caused by 20% of the root causes. Solutions to these root causes are studied and an optimal solution is identified.
Business Solution:
The Statistical Solutions are then converted to do-able practical solutions. Implementation of these Business Solutions is carried out as well. The Improvements are then observed and sustained.
The Six Sigma processes that look at the customer service aspects of a business are outlined in DMADV, which refers to Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, and Verify. DMADV is used when a client or customer requires product improvement, adjustment or creation of an entirely new product or service. DMADV is used for creating a high-quality product keeping in mind customer requirements at every stage of the game.
DMAIC, which refers to Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve and Control, is used in Six Sigma phases to solve both the organizational and the operational issues. DMAIC helps in achieving process improvements by reducing variations. DMAIC is used for reducing many root causes to just a few vital root causes.
Six Sigma is an ‘Industry-Independent’ methodology that is being successfully applied across various industries like Automotive, Aerospace, Health Equipment, FMCG, Electronic Goods, Continuous Process Industries, Textiles, etc. It is also used extensively in Service Industry including Telecom, Banking and Financial Services, Healthcare, Hotels, IT, ITES, KPOs, Airlines, Cargo Movement, Support Services, HR Services, Marketing Services, R&D organizations or in R&D functions of various organizations, etc.
Six Sigma helps organizations produce products and services better, faster and cheaper. It also does the following:
Empower Employees
GE was the 1st company to implement six sigma in services and offshoring, and since then has profited about 2 billion USD.
Qualtec Services has saved over $20 million in two years of using Six Sigma.
1. How can Six Sigma be implemented in small scale industries?
The six sigma methodology can be applied to organizations of any size. It all depends on the nature of the problem faced. In case of a multiple occurring problems, the six sigma would be an optimum use. The problem faced by small-scale enterprises are related to raw material and quality of the output. In these cases, from a Six Sigma pov, Statistical tools like Pareto Analysis will be well-suited and impactful for resolving the problem.
2. What are the different Six Sigma levels?
Sigma level defects per million defects:
3. What are the different kind of variations in Six Sigma?
4. What is the hierarchy of the Six Sigma implementation team?
5. What are the Difference between Yellow, Green, and Black and belt in Six Sigma?
Got a question for us? Please mention them in the comments section and we will get back to you.
Related Posts:
Lean Six Sigma Certification For Starters
 Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP