AWS Solution Architect Certification Training
- 186k Enrolled Learners
- Weekend/Weekday
- Live Class
In the previous blogs, you learnt what is Salesforce and different Salesforce certifications. In this Salesforce tutorial blog, I will show you how to create App in Salesforce. I will be creating an app called StudentForce which can be used to maintain student records.
This app will contain three different objects (tables) to store data. The first object, Students Data, will contain the names of students and their personal details like email ID, phone number, and native city. The second object, College, will store the college students belong to. The third object, Marks, will contain the marks obtained by the students in various subjects.
I have covered the following topics in this Salesforce tutorial blog with step-by-step instructions and screenshots:
Before I get started with creating an app, let me introduce you to the cloud environment where Salesforce apps are built.
The cloud computing space offered to you or your organization by Force.com is called Salesforce org. It is also called Salesforce environment. Developers can create custom Salesforce Apps, objects, workflows, data sharing rules, Visualforce pages and Apex coding on top of Salesforce Org. Get your Salesforce Architect Certification today to become certified.
Learn about Salesforce Cloud Computing here. Now, let us dive deep into Salesforce Apps and understand how they function.
The primary function of a Salesforce app is to manage customer data. Salesforce apps provide a simple UI to access customer records stored in objects (tables). Apps also help in establishing relationship between objects by linking fields.
Apps contain a set of related tabs and objects which are visible to the end user. The below screenshot shows, how the StudentForce app looks like.
The highlighted portion in the top right corner of the screenshot displays the app name: StudentForce. The text highlighted next to the profile pic is my username: Vardhan NS.
Related Learning: What is OWD in Salesforce?
Before you create an object and enter records, you need to set up the skeleton of the app. You can follow the below instructions to set up the app.



In steps 7 and 8, you were asked to choose the relevant tabs and profiles. Tabs and profiles are an integral part of Salesforce Apps because they help you to manage objects and records in Salesforce.
In this salesforce tutorial, I will give you a detailed explanation of Tabs, Profiles and then show you how to create objects and add records to it.
Tabs are used to access objects (tables) in the Salesforce App. They appear on top of the screen and are similar to a toolbar. It contains shortcut links to multiple objects. On clicking the object name in a tab, records in that object will be displayed. Tabs also contain links to external web content, custom pages and other URLs. The highlighted portion in the below screenshot is that of Salesforce tabs.
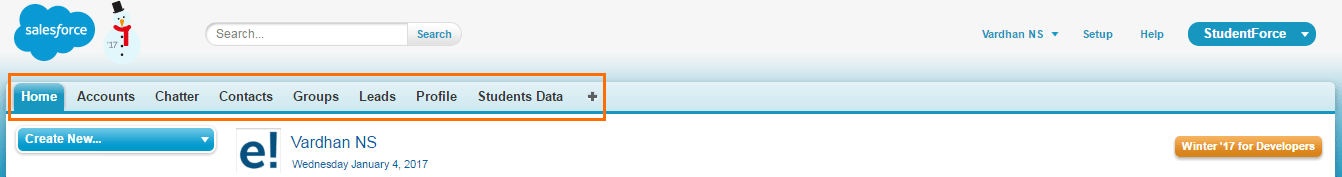
All applications will have a Home tab by default. Standard tabs can be chosen by clicking on ‘+’ in the Tab menu. Accounts, Contacts, Groups, Leads, Profile are the standard tabs offered by Salesforce. For example, Accounts tab will show you the list of accounts in the SFDC org and Contacts tab will show you the list of contacts in the SFDC org.

Besides standard tabs, you can also create custom tabs. Students tab that you see in the above screenshot is a custom tab that I have created. This is a shortcut to reach the custom object: Students.

Every user who needs to access the data or SFDC org will be linked to a profile. A profile is a collection of settings and permissions which controls what a user can view, access and modify in Salesforce.
A profile controls user permissions, object permissions, field permissions, app settings, tab settings, apex class access, Visualforce page access, page layouts, record types, login hour and login IP addresses.
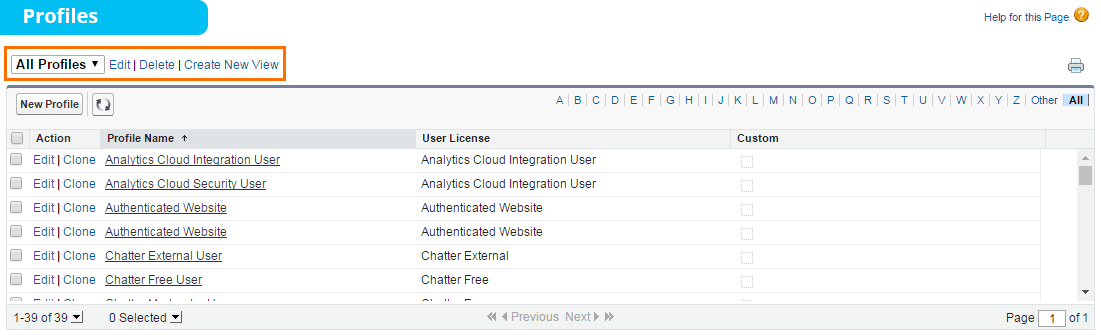
You can define profiles based on the background of the user. For example, different levels of access can be set for different users like system administrator, developer and sales representative.
Similar to tabs, we can use any standard profile or create a custom profile. By default, the available standard profiles are: read only, standard user, marketing user, contract manager, solution manager and system administrator. If you want to create custom profiles, you have to first clone standard profiles and then edit that profile. Do note that one profile can be assigned to many users, but one user cannot be assigned many profiles.
Related Article: Salesforce Interview Questions
Salesforce Tutorial for Beginners
Once the tabs and profiles are set up for your App, you can load data into it. The next section of this Salesforce tutorial will thus cover how data is added to objects in the form of records and fields.
Objects, Fields, and Records are Salesforce’s building blocks. It is important to know what they are and what role they play in building Apps.
Objects are the database tables in Salesforce where data is stored. There are two types of objects in Salesforce:
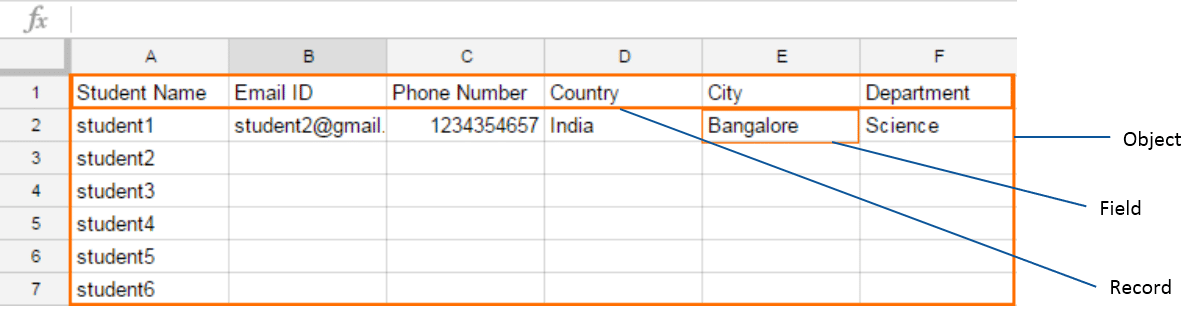
Objects are collections of records, and records are collections of fields.
Related Learning: Record Types in Salesforce
Every row in an object consists of many fields. Thus a record in an object is a combination of related fields. Look at the below excel for illustration.
I will create an object called Students Data which will contain personal details of students.
Steps to create a custom object:

If you want to add this custom object to the tab menu, then you can follow the instructions mentioned earlier in this Salesforce tutorial blog.
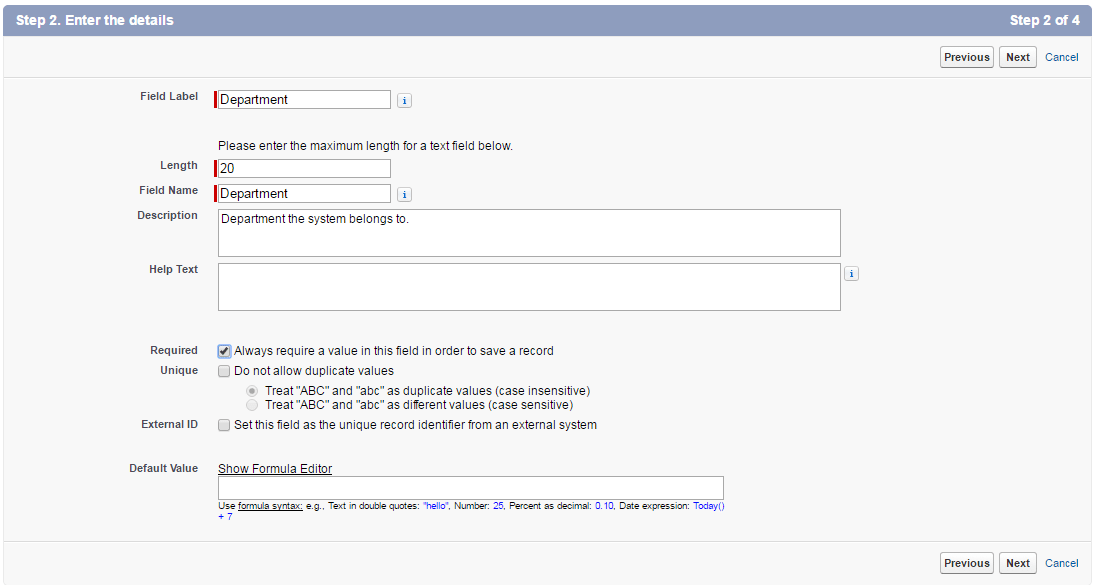
After creating the object, you need to define various fields in it. For example, the fields in a student’s record will be his name, phone number, email ID, department, and native city.
Related Learning: Types of Flows in Salesforce
You can add records to objects only after defining the fields.

As you can see from the below screenshot, there are two types of fields. Standard fields created for every object by default and Custom fields created by myself. The four fields which I have created for Students Data are City, Department, Email ID and Phone No. You will notice that all custom fields are suffixed with ‘__C’ which indicates that you have the power to edit and delete those fields. Whereas some standard fields can be edited, but not deleted.
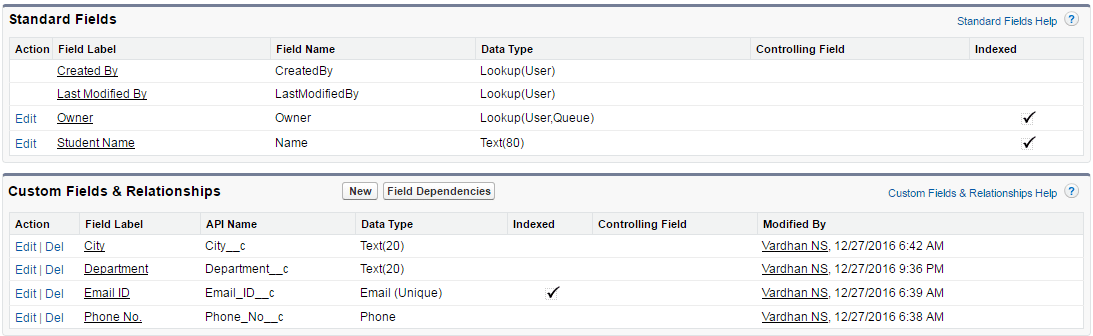
You can now add student records (complete row) to your object.




Data type controls which type of data can be stored in a field. Fields within a record can have different data types. For example:
You can choose any one of the data types for custom fields. Below is a screenshot listing the different data types.

Data types like Lookup Relationship, Master-Detail Relationship and External Lookup Relationship are used to create links/ relationships between one or more objects. Relationships between objects is the next topic of discussion in this Salesforce tutorial blog.
As the name suggests, object relationship is used in Salesforce to create a link between two objects. The question on your mind would be, why is it needed? Let me talk about the need with an example.
In my StudentForce app, there is a Students Data object, which contains personal information of students. Details regarding student’s marks and their previous college are present in different objects. We can use relationships to link these objects using related fields. The marks of the students and colleges can be linked with the Student Name field of Student Data object.
Relationships can be defined while choosing the data type. They are always defined in the child object and are referenced to the common field in master object. Creating such links will help you to search and query data easily when the required data is present in different objects. There are three different types of relationships that can exist between objects. They are:
Let us look into each of them:
Master-Detail relationship is a parent-child relationship in which the master object controls the behaviour of the dependent object. It is a 1:n relationship, in which there can be only one parent, but many children. In my example, Students Data is the master object and Marks is the child object.
Let me give you an example of a Master-Detail relationship. The Students Data object contains student records. Each record contains personal information about a student. However, the marks obtained by students are present in another record called Marks. Look at the screenshot of Marks object below.
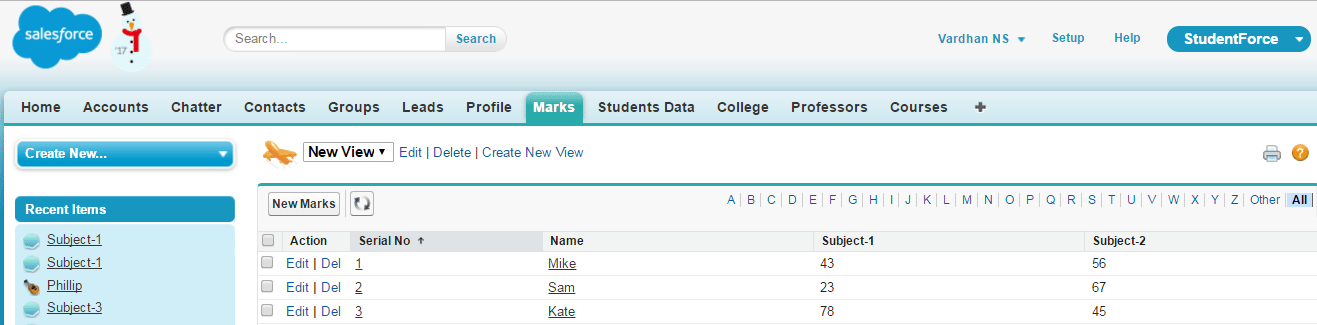
I have created a link between these two objects by using the student’s name. Below are the points you have to keep in mind when setting up a Master-Detail relationship.
You can define master-detail relationships between two custom objects, or between a custom object and standard object as long as the standard object is the master in the relationship.
Lookup relationships are used when you want to create a link between two objects, but without the dependency on the parent object. You can think of this as a form of parent-child relationship where there is only one parent, but many children i.e. 1:n relationship. Below are the points you have to keep in mind when setting up a Lookup relationship.
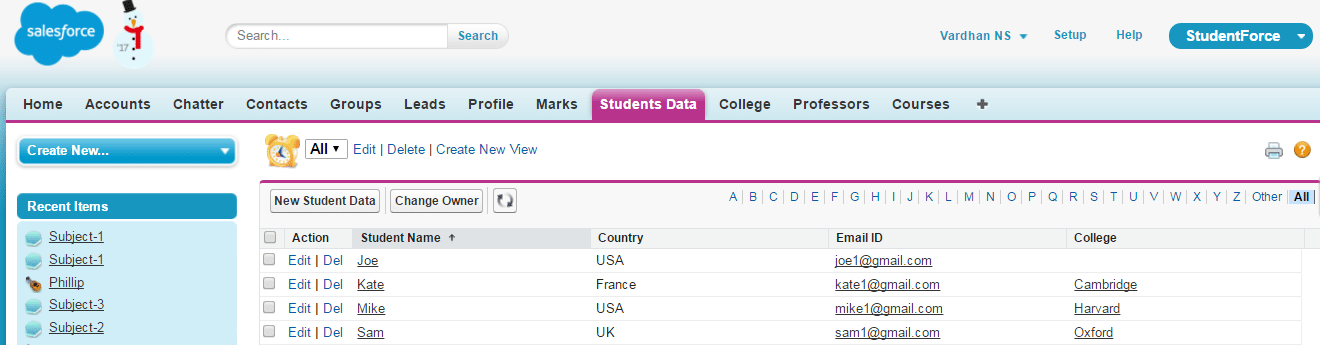
An example of a lookup relationship in my case would be that of a College object. You can see the child object: Students Data in the below screenshot. You will notice that there is an empty College field for the first record. This indicates that the dependency is not a necessity.
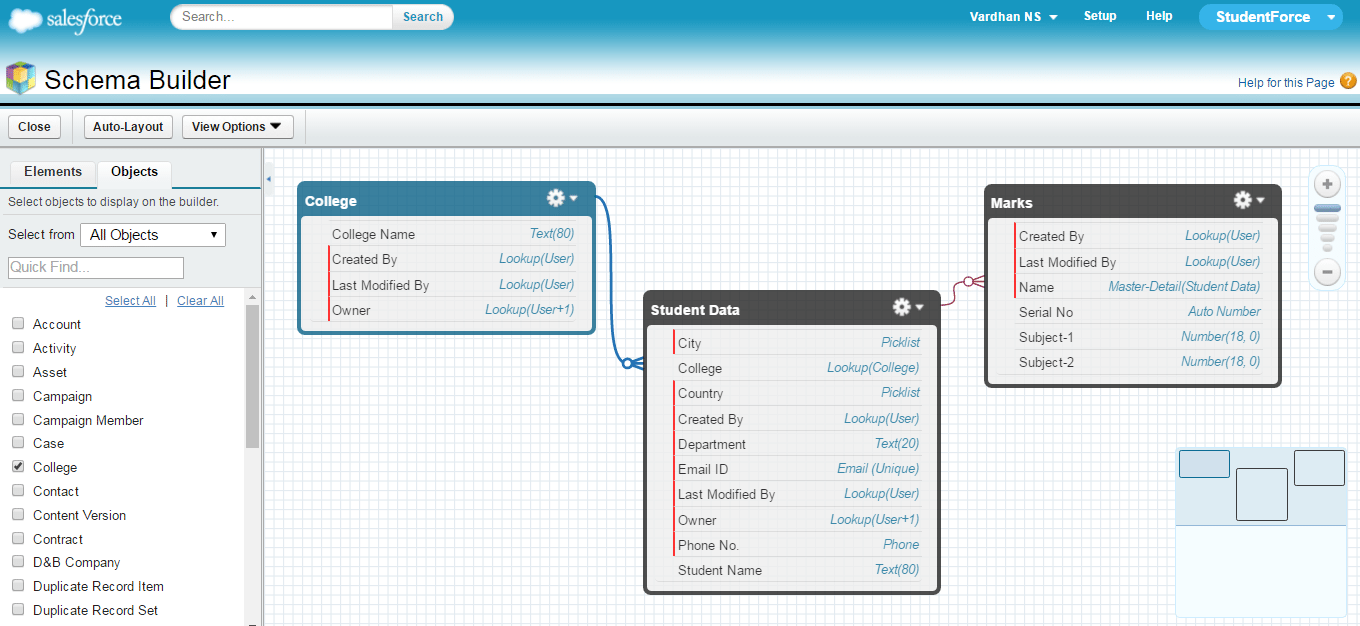
Below is a screenshot of the schema diagram of both the relationships. College – Student Data forms the Lookup relationship and Student Data – Marks forms the Master-Detail relationship.
This is a form of lookup relationship where instead of two tables/ objects, the relationship is within the same table/ object. Hence the name self-relationship. Here, the lookup is referenced to the same table. This relationship is also called Hierarchical relationship.
Salesforce is a cloud-based CRM platform that helps businesses manage customer relationships efficiently. Our Salesforce online training course covers its core features, automation tools, and integration capabilities for career growth.
This kind of a relationship can exist when there is a need to create two master-detail relationships. Two master-detail relationships can be created by linking 3 custom objects. Here, two objects will be master objects and the third object will be dependent on both the objects. In simpler words, it will be a child object for both the master objects.
To give you an example of this relationship, I have created two new objects.
I have created a many-to-many relationship such that every record in the Courses object must have at least one student and at least one professor. This is because every course is a combination of students and professors. In fact, a course, can have one or more number of students and professors associated with them.
Related Learning: Junction Object in Salesforce
The dependency on Student and Professor objects makes Courses as the child object. Student and Professor are thus the master objects. Below is a screenshot of Courses object.
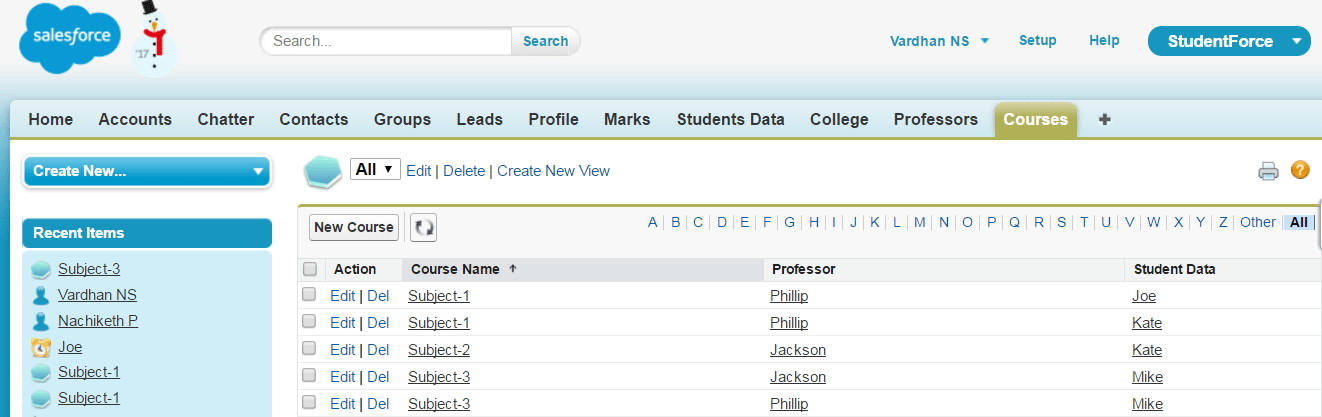
You will notice that there are different combinations of professors and students for these subjects. For example, Kate is associated with two courses and has two different professors for each of those two courses. Mike is associated with only one course, but, has two different professors for that course. Both Joe and Kate are associated with the same course and same professor. In the below screenshot, you will find the schematic diagram of this relationship.
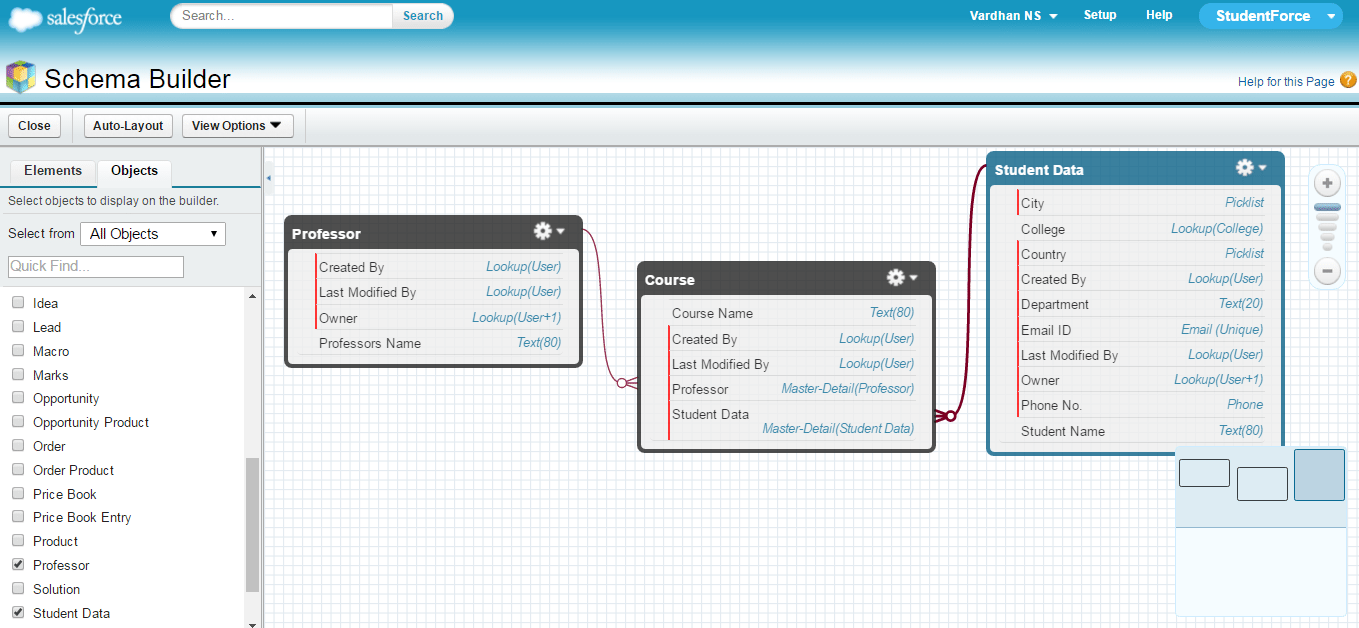
Congrats! The StudentForce App is successfully built. The two schema diagrams present above show how the different objects are linked inside my Salesforce App.
This brings us to the end of this Salesforce tutorial. I hope you understood the various concepts like apps, tabs, profiles, fields, objects and relationships which were explained in this Salesforce tutorial blog. In case you have any doubts or queries, feel free to leave them in the comment section below and I will get back to you at the earliest.
I urge you to see this Salesforce tutorial video that explains the creation of Salesforce student app. Go ahead, enjoy the video and tell me what you think.
Stay tuned to read the next blog in our Salesforce tutorial series. In the meantime, I would suggest you to create a Salesforce account and play around with the Salesforce app. You can try building your own app by following the instructions mentioned above.
If you want to become a professional skilled in Salesforce then, check out our Salesforce Platform Developer1 Certification Course which comes with instructor-led live training and real life project experience.
 Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUPedureka.co
Thank’s for sharing this information. This salesforce tutorial are very easy to understand for a beginner like me. congratulations for this amazing and very helpful website. It really really helpful for me.