AWS Solution Architect Certification Training
- 184k Enrolled Learners
- Weekend/Weekday
- Live Class
From my previous blog, you must have got a basic understanding of Microservice Architecture. But, being a professional with certified expertise in Microservices will require more than just the basics. In this blog, you will get into the depth of the architectural concepts and implement them using an UBER-case study.
You can refer to the What is Microservices, to understand the fundamentals and benefits of Microservices.
It will only be fair if I give you the definition of Microservices.
As such, there is no proper definition of Microservices aka Microservice Architecture, but you can say that it is a framework which consists of small, individually deployable services performing different operations.
Microservices focus on a single business domain that can be implemented as fully independent deployable services and implement them on different technology stacks.
Figure 1: Difference Between Monolithic and Microservice Architecture – Microservice Architecture
Refer to the diagram above to understand the difference between monolithic and microservice architecture. For a better understanding of differences between both the architectures, you can refer to my previous blog What Is Microservices
To make you understand better, let me tell you some key concepts of microservice architecture.
Before you start building your own applications using microservices you need to be clear about the scope, and functionalities of your application.
Following are some guidelines to be followed while discussing microservices.
Guidelines While Designing Microservices
Now, that you have read through the basic guidelines while designing microservices, let’s understand the architecture of microservices.
A typical Microservice Architecture (MSA) should consist of the following components:
Refer to the diagram below.
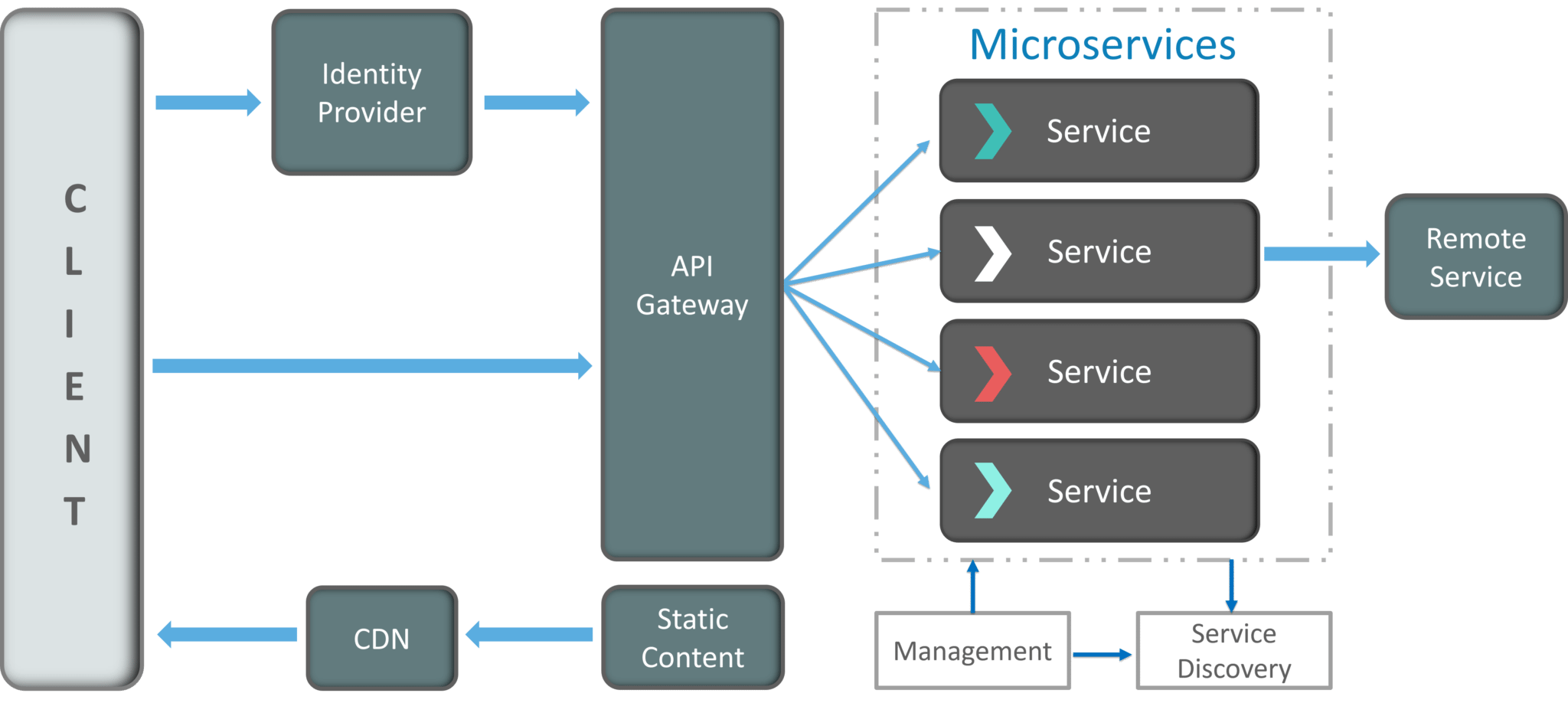
Figure 2: Architecture Of Microservices – Microservice Architecture
I know the architecture looks a bit complex, but let me simplify it for you.
1. Clients
The architecture starts with different types of clients, from different devices trying to perform various management capabilities such as search, build, configure etc.
2. Identity Providers
These requests from the clients are then passed on the identity providers who authenticate the requests of clients and communicate the requests to API Gateway. The requests are then communicated to the internal services via well-defined API Gateway.
3. API Gateway
Since clients don’t call the services directly, API Gateway acts as an entry point for the clients to forward requests to appropriate microservices.
The advantages of using an API gateway include:
After receiving the requests of clients, the internal architecture consists of microservices which communicate with each other through messages to handle client requests.
4. Messaging Formats
There are two types of messages through which they communicate:
The next question that may come to your mind is how do the applications using Microservices handle their data?
5. Data Handling
Well, each Microservice owns a private database to capture their data and implement the respective business functionality.Also, the databases of Microservices are updated through their service API only. Refer to the diagram below:
 Figure 3: Representation Of Microservices Handling Data – Microservice Architecture
Figure 3: Representation Of Microservices Handling Data – Microservice Architecture
The services provided by Microservices are carried forward to any remote service which supports inter-process communication for different technology stacks.
6. Static Content
After the Microservices communicate within themselves, they deploy the static content to a cloud-based storage service that can deliver them directly to the clients via Content Delivery Networks (CDNs).
Apart from the above components, there are some other components appear in a typical Microservices Architecture:
7. Management
This component is responsible for balancing the services on nodes and identifying failures.
8. Service Discovery
Acts as a guide to Microservices to find the route of communication between them as it maintains a list of services on which nodes are located.
Now, let’s look into the pros and cons of this architecture to gain a better understanding of when to use this architecture.
Refer to the table below.
| Pros Of Microservice Architecture | Cons Of Microservice Architecture |
| Freedom to use different technologies | Increases troubleshooting challenges |
| Each microservice focuses on single business capability | Increases delay due to remote calls |
| Supports individual deployable units | Increased efforts for configuration and other operations |
| Allows frequent software releases | Difficult to maintain transaction safety |
| Ensures security of each service | Tough to track data across various service boundaries |
| Multiple services are parallelly developed and deployed | Difficult to move code between services |
Let us understand more about Microservices by comparing UBER’s previous architecture to the present one.
UBER’s Previous Architecture
Like many startups, UBER began its journey with a monolithic architecture built for a single offering in a single city. Having one codebase seemed cleaned at that time, and solved UBER’s core business problems. However, as UBER started expanding worldwide they rigorously faced various problems with respect to scalability and continuous integration.
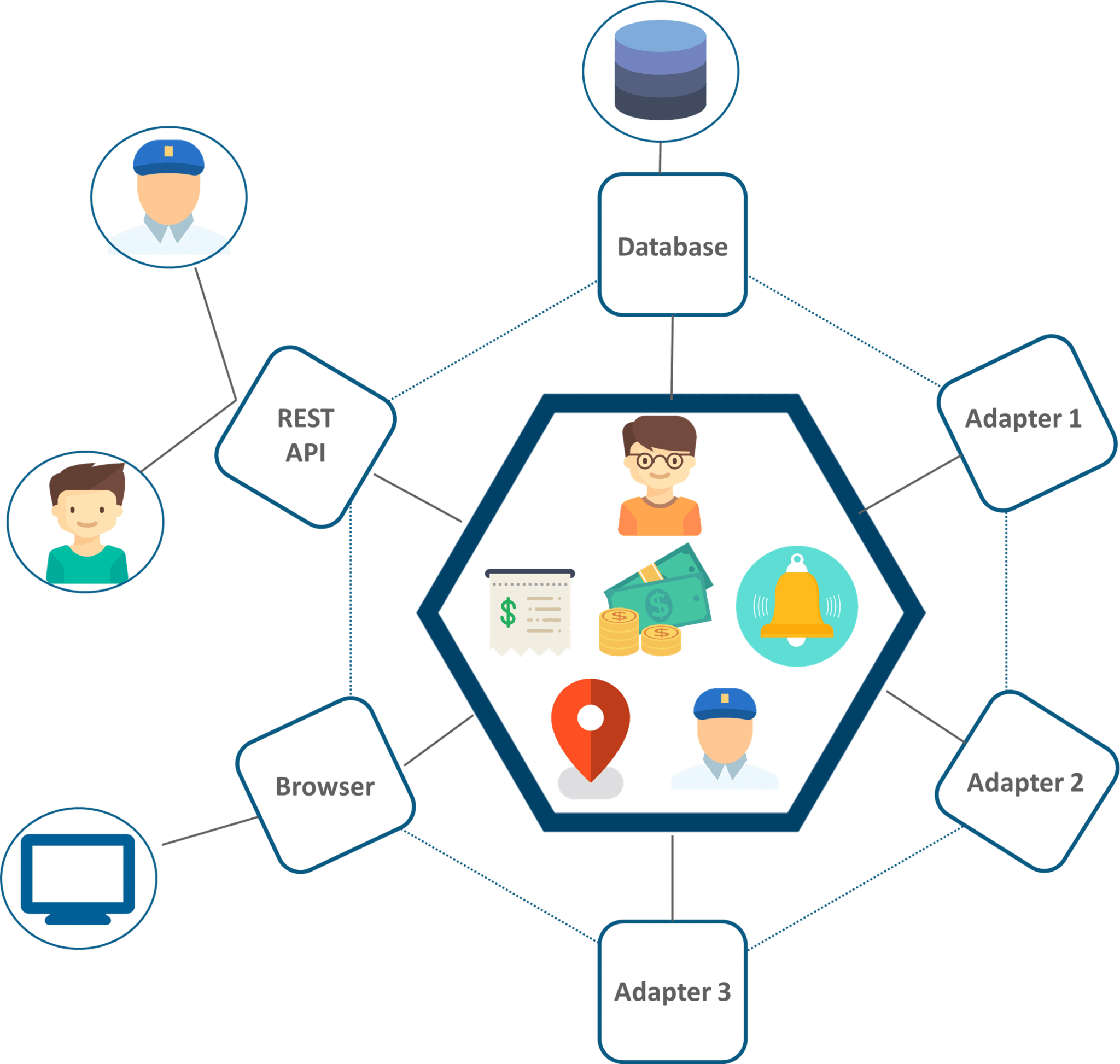
Figure 4: Monolithic Architecture Of UBER – Microservice Architecture
The above diagram depicts UBER’s previous architecture.
So, if you notice here all the features such as passenger management, billing, notification features, payments, trip management and driver management were composed within a single framework.
Problem Statement
While UBER started expanding worldwide this kind of framework introduced various challenges. The following are some of the prominent challenges
Solution
To avoid such problems UBER decided to change its architecture and follow the other hyper-growth companies like Amazon, Netflix, Twitter and many others. Thus, UBER decided to break its monolithic architecture into multiple codebases to form a microservice architecture.
Refer to the diagram below to look at UBER’s microservice architecture.
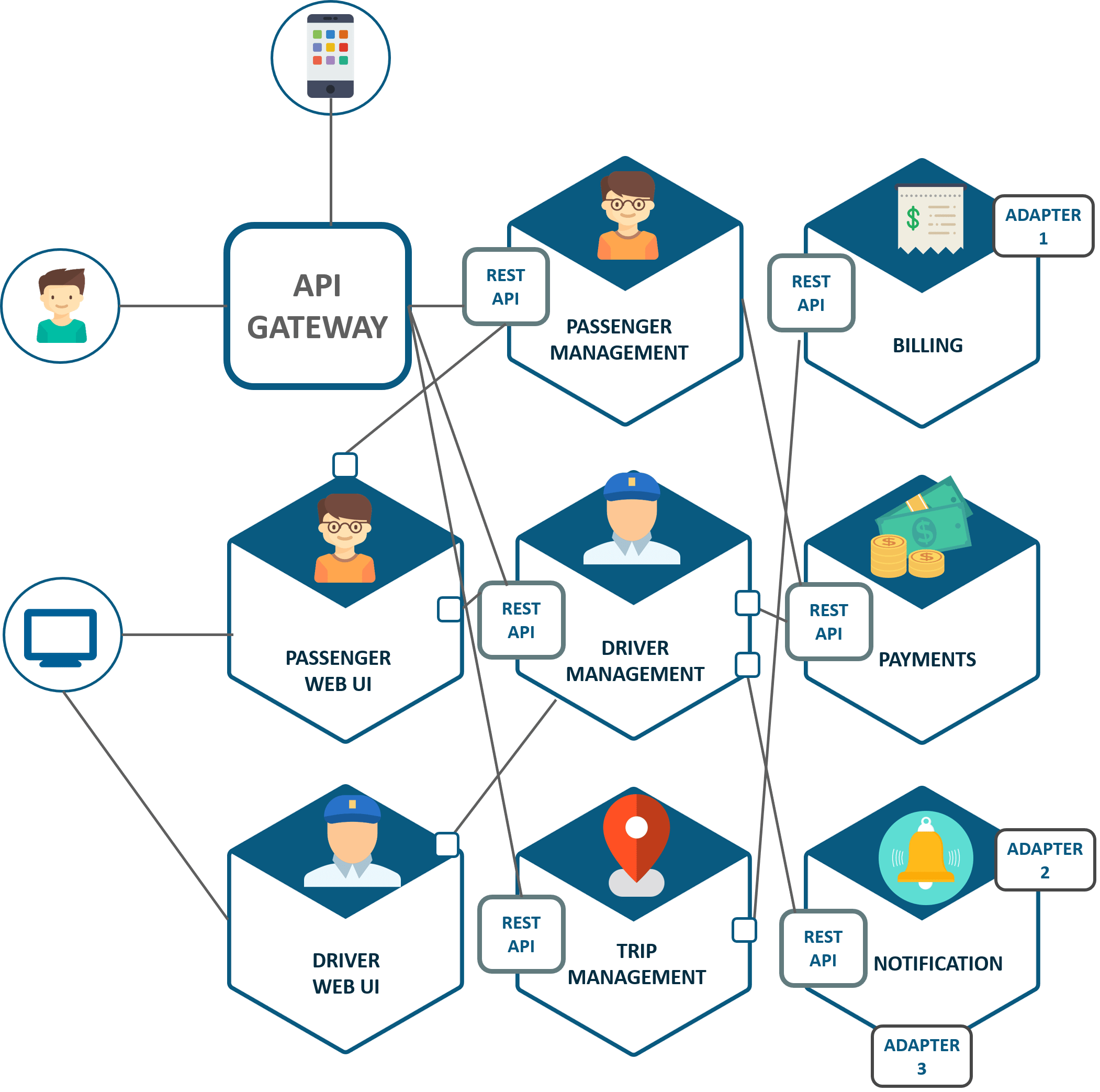
Figure 5: Microservice Architecture Of UBER – Microservice Architecture
In this way, UBER benefited by shifting its architecture from monolithic to Microservices.
I hope you have enjoyed reading this post on Microservice Architecture. I will be coming up with more blogs, which will contain hands-on as well.
If you wish to learn Microservices and build your own applications, then check out our Microservices Training which comes with instructor-led live training and real-life project experience. This training will help you understand Microservices in depth and help you achieve mastery over the subject.
Got a question for us? Please mention it in the comments section of ” Microservice Architecture” and I will get back to you.
 Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUPedureka.co
Very Helpful example. Thanks for sharing
Hey Sanjoy, thank you for appreciating our work. Stay tuned for similar updates in the future. Cheers :)
Looks perfect. Great work!
Hey Rohit, we are glad that you liked our blog. Do browse through our channel to find more such blogs. Cheers :)