Full Stack Development Internship Program
- 29k Enrolled Learners
- Weekend/Weekday
- Live Class
Node.js, the server-side scripting tool, using which one can build everything, starting from a simple command line programs to the complex enterprise level web applications with equal ease. This is why most industries demand a Certified Node.js Developer to manage the entire server side. Node.js, also brings with it, career opportunities at various levels. In case you are planning to attend Node.js interviews in the near future, we are here to help you with a list of Top 50 Node.js interview questions that you must prepare in 2025.
In this Node.js interview questions article, I have divided the questions into 3 segments based on their difficulty level:
Before I start off with this Node.js Interview Questions article, let me put forth a request to the readers who might have attended Node.js interviews in recent past. So, if you have come across such questions which were asked in interviews but are missing in this article, feel free to put those questions in the comment section below. We will try and answer those at the earliest so that others can also benefit from it.
Now, let’s get started.
| Features | JavaScript | Node.js |
| Type | Programming Language | Interpreter and environment for JavaScript |
| Utility | Used for any client-side activity for a web application | Used for accessing or performing any non-blocking operation of any operating system |
| Running Engine | Spider monkey (FireFox), JavaScript Core (Safari), V8 (Google Chrome), etc. | V8 (Google Chrome) |
Node.js is an extremely powerful framework developed on Chrome’s V8 JavaScript engine that compiles the JavaScript directly into the native machine code. It is a lightweight framework used for creating server-side web applications and extends JavaScript API to offer usual server-side functionalities. It is generally used for large-scale application development, especially for video streaming sites, single page application, and other web applications.
| Features | Description |
| Fast | Node.js is built on Google Chrome’s V8 JavaScript Engine which makes its library very fast in code execution |
| Asynchronous | Node.js based server never waits for an API to return data thus making it asynchronous |
| Scalable | It is highly scalable because of its event mechanism which helps the server to respond in a non-blocking way |
| Open Source | Node.js has an extensive open source community which has contributed in producing some excellent modules to add additional capabilities to Node.js applications |
| No Buffering | Node.js applications simply output the data in chunks and never buffer any data |
| Angular | Node.js |
| 1. It is an open source web application development framework | 1. It is a cross-platform run-time environment for applications |
| 2. It is written in TypeScript | 2. It is written in C, C++ and JavaScript languages |
| 3. Used for building single-page client-side web applications | 3. Used for building fast and scalable server-side networking applications |
| 4. Angular itself is a web application framework | 4. Node.js has many different frameworks like Sails.js, Partial.js, and Express.js, etc. |
| 5. Ideal for creating highly active and interactive web apps | 5. Ideal for developing small size projects |
| 6. Helpful in splitting an app into MVC components | 6. Helpful in generating database queries |
| 7. Suitable for developing real-time applications | 7. Suitable in situations where something faster and more scalable is required |
Node.js uses a single threaded model in order to support async processing. With async processing, an application can perform better and is more scalable under web loads. Thus, Node.js makes use of a single-threaded model approach rather than typical thread-based implementation.
Node.js is a virtual machine that uses JavaScript as its scripting language and runs on a v8 environment. It works on a single-threaded event loop and a non-blocking I/O which provides high rate as it can handle a higher number of concurrent requests. Also, by making use of the ‘HTTP’ module, Node.js can run on any stand-alone web server.
Node.js can be used to develop:
There are two types of API functions in Node.js:
| Asynchronous | Non-blocking |
| Asynchronous means not synchronous. Using these we can make asynchronous HTTP requests that do not wait for the server to respond. These functions continue to respond to the request for which it has already received the server response. | Non-blocking functions are used in regards with I/O operations. They immediately respond with whatever data is available and keeps on running as per the requests. In case, any answer couldn’t be retrieved then the API returns immediately with an error. |
In case you are facing any challenges with these Node.js Interview Questions, please mention your problems in the section comment section below.
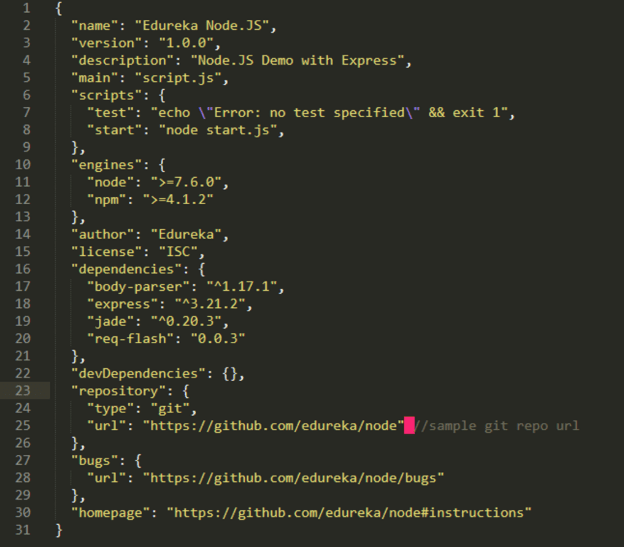
The package.json file in Node.js is the heart of the entire application. It is basically the manifest file that contains the metadata of the project where we define the properties of a package.
 11. What do you understand by Event-driven programming?
11. What do you understand by Event-driven programming?Event-driven programming is an approach that heavily makes use of events for triggering various functions. An event can be anything like a mouse click, key press, etc. When an event occurs, a call back function is executed that is already registered with the element. This approach mainly follows the publish-subscribe pattern. Because of event-driven programming, Node.js is faster when compared to other technologies.
An event loop in Node.js handles all the asynchronous callbacks in an application. It is one of the most important aspects of Node.js and the reason behind Node.js have non-blocking I/O. Since Node.js is an event-driven language, you can easily attach a listener to an event and then when the event occurs the callback will be executed by the specific listener. Whenever functions like setTimeout, http.get, and fs.readFile are called, Node.js executed the event loop and then proceeds with the further code without waiting for the output. Once the entire operation is finished, Node.js receives the output and then executes the callback function. This is why all the callback functions are placed in a queue in a loop. Once the response is received, they are executed one by one.
REPL in Node.js stands for Read, Eval, Print, and Loop. It represents a computer environment such as a window console or Unix/Linux shell where any command can be entered and then the system can respond with an output. Node.js comes bundled with a REPL environment by default. REPL can perform the below-listed tasks:
Below is the list of the tasks which must be done asynchronously using the event loop:
This Edureka video on will introduce you to all the popular and trending technologies in the market which you should focus on in 2025. These are the trending technologies that you need to learn in order to have a successful career in the year 2025.
A test pyramid basically is a diagram that describes the ratio of how many unit tests, integration tests, and end-to-end test are required to be written for the successful development of the project.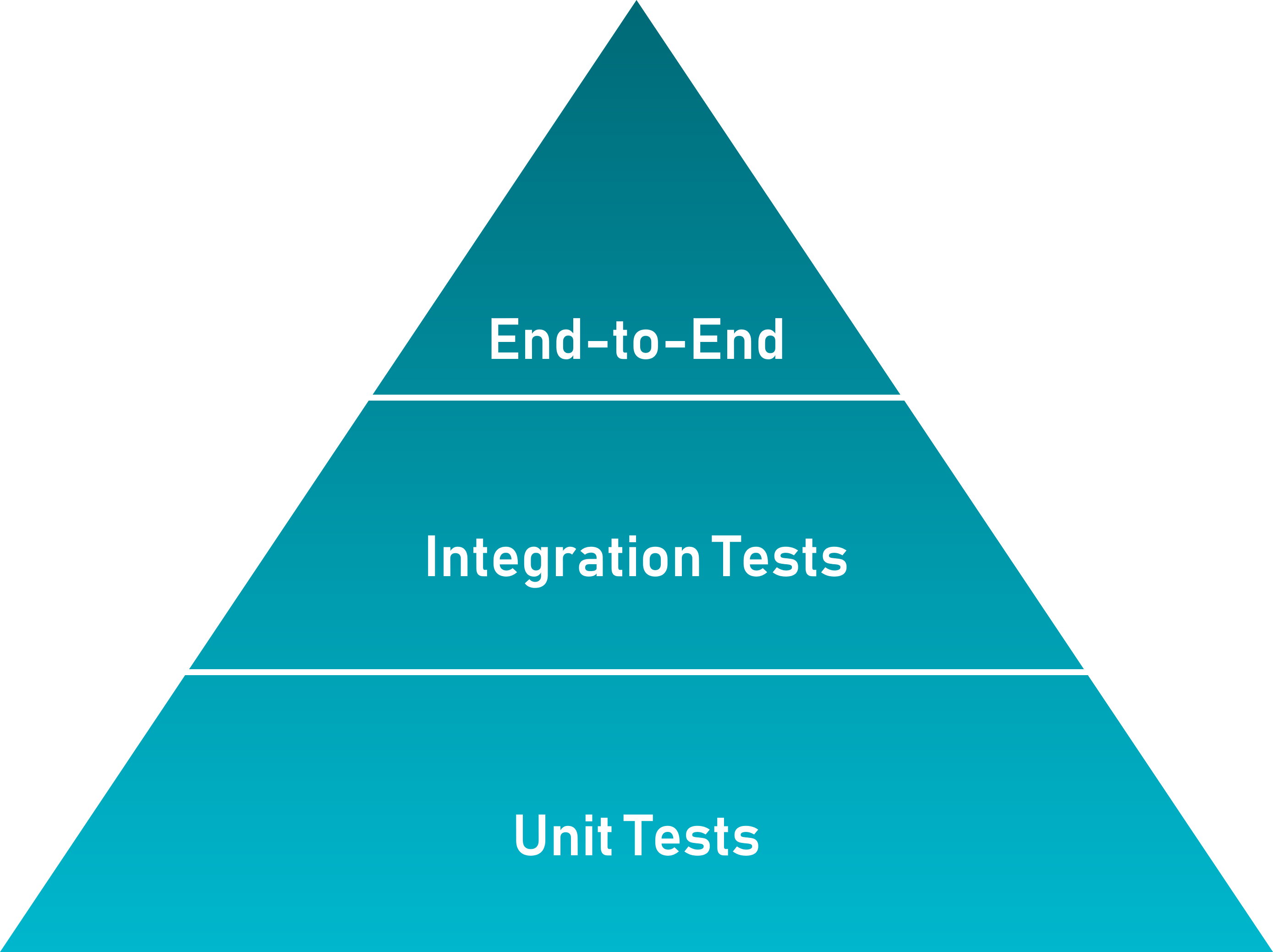
Error-first callbacks in Node.js are used to pass errors and data. The very first parameter you need to pass to these functions has to be an error object while the other parameters represent the associated data. Thus you can pass the error object for checking if anything is wrong and handle it. In case there is no issue, you can just go ahead and with the subsequent arguments.
var myPost = new Post({title: 'edureka'});
myPost.save(function(err,myInstance){
if(err){
//handle error and return
}
//go ahead with `myInstance`
});A module in Node.js is used to encapsulate all the related codes into a single unit of code which can be interpreted by shifting all related functions into a single file. For example, suppose you have a file called greet.js that contains the two functions as shown below:
module.exports = {
greetInHindi: function(){
return "NAMASTE";
},
greetInKorean: function(){
return "ANNYEONGHASEYO";
}};As you can see module.exports provide two functions which can be imported in another file using below code:
var eduGreets = require ("./greet.js");
eduGreets.greetInHindi() //NAMASTE
eduGreets.greetInKorean() //ANNYEONGHASEYOReactor Pattern in Node.js is basically a concept of non-blocking I/O operations. This pattern provides a handler that is associated with each I/O operation and as soon as an I/O request is generated, it is then submitted to a demultiplexer. This demultiplexer is a notification interface which is capable of handling concurrency in non-blocking I/O mode. It also helps in collecting each and every request in the form of an event and then place each event in a queue. Thus resulting in the generation of the Event Queue. Simultaneously, we have our event loop which iterates the events present in the Event Queue.
| Front-end Development | Back-end Development |
| 1. Uses mark up and web languages like HTML, CSS, JavaScript | 1. Uses programming and scripting languages like Python, Ruby, Perl, etc. |
| 2. Based on asynchronous requests and AJAX | 2. Based on Server Architecture |
| 3. Better Accessibility | 3. Enhanced Security |
| 4. Used for SEO | 4. Used for Backup |
LTS stands Long Term Support version of Node.js that receives all the critical bug fixes along with security updates and performance improvements. These versions are supported for at least 18 months and mainly focus on stability and security. The modifications done to the LTS versions are restricted to the bug fixes, security upgrade, npm, and documentation updates, performance improvement, etc.
Major security implementations in Node.js are:
Callback Hell is also known as the Pyramid of Doom. It is a pattern caused by intensively nested callbacks which are unreadable and unwieldy. It typically contains multiple nested callback functions which in turn make the code hard to read and debug. It is caused by improper implementation of the asynchronous logic.
async_A(function(){
async_B(function(){
async_C(function(){
async_D(function(){
....
});
});
});
});In case you are facing any challenges with these Node.js Interview Questions, please mention your problems in the section comment section below.
Libuv is a multi-platform support library of Node.js which majorly is used for asynchronous I/O. It was primarily developed for Node.js, with time it is popularly practiced with other systems like as Luvit, pyuv, Julia, etc. Libuv is basically an abstraction around libev/ IOCP depending on the platform, providing users an API based on libev. A few of the important features of libuv are:
In general, middleware is a function receives the Request and Response objects. In other words, in an application’s request-response cycle these functions have access to various request & response objects along with the next function of the cycle. The next function of middleware is represented with the help of a variable, usually named next. Most commonly performed tasks by the middleware functions are:
The URL module of Node.js provides various utilities for URL resolution and parsing. It is a built-in module that helps in splitting up the web address into a readable format:
var url = require('url');For example:
var url = require('url');
var adrs = 'http://localhost:8082/default.htm?year=2019&month=april';
var q = url.parse(adr, true);
console.log(q.host); //returns 'localhost:8082'
console.log(q.pathname); //returns '/default.htm'
console.log(q.search); //returns '?year=2019 and month=april'
var qdata = q.query; //returns an object: { year: 2019, month: 'april' }
console.log(qdata.month); //returns 'april'ESLint is an open source project initially developed by Nicholas C. Zakas in 2013 which aims to provide a linting utility for JavaScript through a plug. Linters in Node.js are good tools for searching certain bug classes, especially those which are related to the variable scope.
Google uses V8 as it is a Chrome runtime engine that converts JavaScript code into native machine code. This, in turn, speeds up the application execution and response process and give you a fast running application.
In Node.js, the control flow function is basically the code that is executed between the asynchronous function calls. Below are the steps that must be followed for executing it:
Below are the two arguments that async.queue takes as input:
In Node.js, the spawn() is used to launch a new process with the provided set of commands. This method doesn’t create a new V8 instance and just one copy of the node module is active on the processor. When your child process returns a large amount of data to the Node you can invoke this method.
Syntax:
child_process.spawn(command[, args][, options])
Whereas, the fork() in Node.js is a special instance of spawn() that executes a new instance of the V8 engine. This method simply means that multiple workers are running on a single Node code base for various task.
Syntax:
child_process.fork(modulePath[, args][, options])
In case you are facing any challenges with these Node.js Interview Questions, please mention your problems in the section comment section below.
In Node.js, Globals are the objects which are global in nature and are available in all the modules of the application. You can use these objects directly in your application, rather than having to include them explicitly. The global objects can be modules, functions, strings, object, etc. Moreover, some of these objects can be in the module scope instead of global scope.
In Node.js, stubs are basically the programs or functions that are used for stimulating the module or component behavior. During any test cases, stubs provide the canned answers of the functions.
In Node.js, assert is used to write tests. It only provides feedback only when any of the running test cases fails. This module gives you a set of assertion tests which are then used for testing invariants. It is basically used internally by Node.js but using require(‘assert’) code, it can be used in other applications as well.
var assert = require('assert');
function mul(a, b) {
return a * b;
}
var result = mul(1,2);
assert( result === 2, 'one multiplied by two is two');The test pyramid is basically a concept that is developed by Mike Cohn. According to this, you should have a higher number of low-level unit tests as compared to high-level end-to-end tests that running through a GUI.
In terms of HTTP APIs it may be defined as:
Express.js is a framework built on top of Node.js that facilitates the management of the flow of data between server and routes in the server-side applications. It is a lightweight and flexible framework that provides a wide range of features required for the web as well as mobile application development. Express.js is developed on the middleware module of Node.js called connect. The connect module further makes use of http module to communicate with Node.js. Thus, if you are working with any of the connect based middleware modules, then you can easily integrate with Express.js.
In Node.js, process.nextTick() and setImmediate(), both are functions of the Timers module which help in executing the code after a predefined period of time. But these functions differ in their execution. The process.nextTick function waits for the execution of action till the next pass around in the event loop or once the event loop is completed only then it will invoke the callback function. On the other hand, setImmediate() is used to execute a callback method on the next cycle of the event loop which eventually returns it to the event loop in order to execute the I/O operations.
Buffer class in Node.js is used for storing the raw data in a similar manner of an array of integers. But it corresponds to a raw memory allocation that is located outside the V8 heap. It is a global class that is easily accessible can be accessed in an application without importing a buffer module. Buffer class is used because pure JavaScript is not compatible with binary data. So, when dealing with TCP streams or the file system, it’s necessary to handle octet streams.
In general, Node.js is a single threaded process and doesn’t expose the child threads or thread management methods. But you can still make use of the child threads using spawn() for some specific asynchronous I/O tasks which execute in the background and don’t usually execute any JS code or hinder with the main event loop in the application. If you still want to use the threading concept in your application you have to include a module called ChildProcess explicitly.
Streams in Node.js are the collection of data similar to arrays and strings. They are objects using which you can read data from a source or write data to a destination in a continuous manner. It might not be available at once and need not to have fit in the memory. These streams are especially useful for reading and processing a large set of data. In Node.js, there are four fundamental types of streams:
If the project is in the production stage, Node.js promotes the convention of making use of NODE_ENV variable to flag it. This helps in taking better judgment during the development of the projects. Also, when you set your NODE_ENV to production, your application tends to perform 3 times faster.
Node.js provides two ways to read and execute files which are using readFile and CreateStream. readFile() is a fully buffered process which returns the response only when the complete file is pushed into the buffer and is read. It is a memory intensive process and in case of large files, the processing can be very slow. Whereas createReadStream is a partially buffered which treats the entire process as an event series. The entire file is split into chunks which are then processed and sent back as a response one by one. Once done, they are finally removed from the buffer. Unlike readFile, createReadStream is really effective for the processing of the large files.
Node.js provides a Timers module which contains various functions for executing the code after a specified period of time. Below I have listed down the various functions provided by this module:
In Node.js, Punycode is an encoding syntax that is used for converting Unicode (UTF-8) string of characters into a basic ASCII string of characters. It is important as the hostnames can only understand the ASCII characters. Thus, Node.js version 0.6.2 onwards, it was bundled up with the default Node package. If you want to use it with any previous versions, you can easily do that by using the following code:
punycode = require('punycode');The most basic difference between Node.js and Ajax that, Node.js is a server-side JavaScript whereas Ajax is a client-side technology. In simpler terms, Ajax is mostly used for updating or modifying the webpage contents without having to refresh it. On the other hand, Node.js is required to develop the server software that are typically executed by the servers instead of the web browsers.
Node.js do provide a simple TCP based protocol and debugging client that comes built-in. In order to debug your JavaScript file, you can use the below debug argument followed by js file name that you want to debug.
Syntax:
node debug [script.js | -e "script" | <host> : <port> ]In case you are facing any challenges with these Node.js Interview Questions, please mention your problems in the section comment section below.
 Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUPedureka.co
I don’t agree with your answer for Qn.20;
Scalability is baked into node; Using the inbuit ‘cluster’ module,you can make use of multi core hardware and scale accordingly.
Biggest drawback of node.js, in my opinion, is that it is not the right choice when high intensive CPU operations are involved.
elaborate event-driven programming with an example
Hey Girish, thanks for checking out our blog. Node.js uses events heavily and it is also one of the reasons why Node.js is pretty fast compared to other similar technologies. As soon as Node starts its server, it simply initiates its variables, declares functions and then simply waits for the event to occur.
In an event-driven application, there is generally a main loop that listens for events, and then triggers a callback function when one of those events is detected.
https://uploads.disquscdn.com/images/36658e0c42f421578809ddadc864ee6fac5cea8dbd29f043b5888eca6fbca78e.png
Now create a program and name it as sample.js
// Import events module
var events = require(‘events’);
// Create an eventEmitter object
var eventEmitter = new events.EventEmitter();
// Create an event handler as follows
var connectHandler = function connected() {
console.log(‘connection succesful.’);
// Fire the data_received event
eventEmitter.emit(‘data_received’);
}
// Bind the connection event with the handler
eventEmitter.on(‘connection’, connectHandler);
// Bind the data_received event with the anonymous function
eventEmitter.on(‘data_received’, function(){
console.log(‘data received succesfully.’);
});
// Fire the connection event
eventEmitter.emit(‘connection’);
console.log(“Program Ended.”);
Now run the code
$ mnode sample.js
Now the output will be :-
connection successful.
data received successfully.
Program Ended.
Hope this helps. Cheers!
Thanks. Really helpful
Thanks Swati. We are so happy we could help. Do keep checking back in for more blogs on all your favourite topics.