Full Stack Development Internship Program
- 29k Enrolled Learners
- Weekend/Weekday
- Live Class
HashSet in Java is one of the most important aspects of Java Collection hierarchy. It is typically used to store unique values in an unordered manner. Through the medium of this article on HashSet in Java, I will be giving you a complete walkthrough of what exactly is a HashSet and how you can use it in your application.
Below are the topics covered in this article:
Let’s get started by first understanding what are HashSet in Java.
HashSet in Java
java.util.HashSet class is a member of the Java collections framework which inherits the AbstractSet class and implements the Set interface. It implicitly implements a hashtable for creating and storing a collection of unique elements. Hashtable is nothing but an instance of the HashMap class that uses a hashing mechanism for storing the information within a HashSet.
Hashing is the process of converting the informational content into a unique value that is more popularly known as hash code. This hashcode is then used for indexing the data associated with the key. The entire process of transforming the informational key into the hashcode is performed internally.
Now for a better understanding of HashSet in Java, let me list down a few of its features:
Now that you are aware of what exactly is HashSet in Java, let’s move further with this article and demystify the differences between HashMap and HashSet in Java.
Now that you have a clear distinction between HashMap and HashSet, let’s now focus on HashSet again and dive deeper into it. In the next section of this article, I will be introducing you to the complete hierarchy of HashSet in Java.
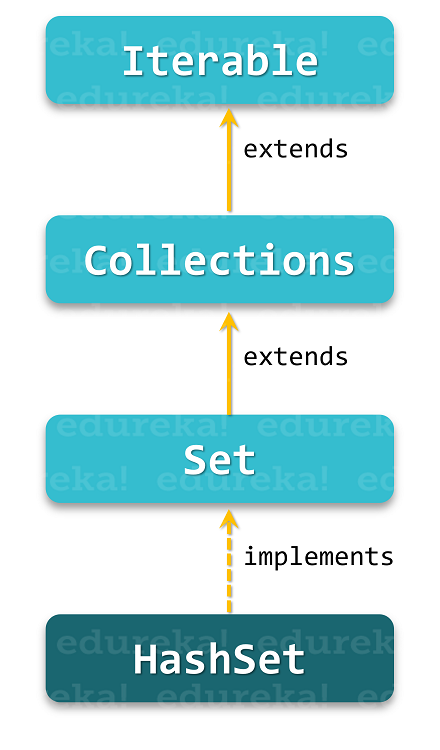
As you can see from the below-given diagram, The HashSet class implements the Set interface. The Set interface further inherits the Collection interface which eventually extends the Iterable interface in a hierarchical order.
Now, moving ahead with this HashSet in Java article, let’s us check out the various constructors supported by this class.
These were the four constructors of the HashSet class in Java. Let’s now find out what are the various methods defined in Java HashSet.
Along with the above-listed methods, the HashSet class in Java also contains the methods inherited from its superclasses.
Let’s now try implementing these methods and get our feet wet with coding.
In the below example, we will try and implement a number of methods provided by the HashSet class.
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.*;
public class SampleHashSet {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating a HashSet
Set<String> eduCourses = new HashSet<>();
// Adding new elements to the HashSet
eduCourses.add("Big Data");
eduCourses.add("Node.js");
eduCourses.add("Java");
eduCourses.add("Python");
eduCourses.add("Blockchain");
eduCourses.add("JavaScript");
eduCourses.add("Selenium");
eduCourses.add("AWS");
eduCourses.add("Machine Learning");
eduCourses.add("RPA");
// Adding duplicate elements will be ignored
eduCourses.add("Java");
eduCourses.add("RPA");
System.out.println(eduCourses);
// Check if the HashSet contains an specific element
String myCourse = "Node.js";
if(eduCourses.contains(myCourse)) {
System.out.println(myCourse + " is in the courses list.");
} else {
System.out.println(myCourse + " is not in the courses list.");
}
// Sorting eduCourses using List
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(eduCourses);
Collections.sort(list);
// Printing the sorted elements of the HashSet
System.out.println("Printing the Courses in sorted order using List: " + list);
// Removing items from HashSet using remove()
eduCourses.remove("Python");
// Iterating over HashSet items
System.out.println("Iterating over course list after removing Python:");
Iterator<String> i = eduCourses.iterator();
while (i.hasNext())
System.out.println(i.next());
// Creating another object of HashSet
HashSet<String> eduNewCourses = new HashSet<String>();
eduNewCourses.add("Node.js");
eduNewCourses.add("Python");
eduNewCourses.add("Machine Learning");
//Removing all the new elements from HashSet
eduCourses.removeAll(eduNewCourses);
System.out.println("After invoking removeAll() method courses left: "+ eduCourses);
//Removing elements on the basis of specified condition
eduCourses.removeIf(str->str.contains("Java"));
System.out.println("After invoking removeIf() method: "+ eduCourses);
// Removing elements from eduCourses which are specified in eduNewCourses
eduCourses.retainAll(eduNewCourses);
System.out.println("HashSet after " + "retainAll() operation : " + eduNewCourses);
//Removing all the elements available in the set
eduCourses.clear();
System.out.println("After invoking clear() method: "+ eduCourses);
}
}When you execute the above code, it will give you the below-shown output.
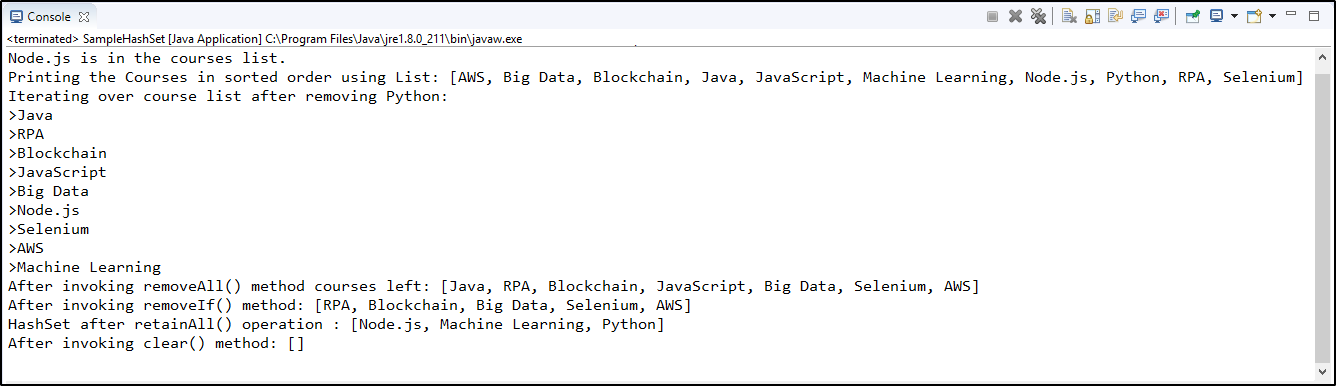
With this, we come to the end of this article. Hope I was able to keep the concepts crisp and clear. You can learn more about Java Collections by going through our other Java blogs.
Now that you have understood what is a HashSet in Java, check out the Java Certification Training by Edureka, a trusted online learning company with a network of more than 250,000 satisfied learners spread across the globe. Edureka’s Java J2EE and SOA training and certification course is designed for students and professionals who want to be a Java Developer. The course is designed to give you a head start into Java programming and train you for both core and advanced Java concepts along with various Java frameworks like Hibernate & Spring.
Got a question for us? Please mention it in the comments section of this “HashSet in Java” article and we will get back to you as soon as possible.
 Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUPedureka.co