Demand Sensing: Companies now confront supply chain issues due to shortening product lifecycles and massive amounts of data. Above this, suppliers deal with erratic clients and increase demand pattern volatility. Brands need to anticipate these changes in demand to be ready for potential issues. Using this expertise, they may ensure that they meet clients’ requirements at the appropriate moment.
A systematic approach to demand planning is now more important than ever since it helps companies deliver the right items to the appropriate consumers faster by gaining in-depth knowledge of their needs. Some of the finest techniques include numerous layers in a demand forecasting and sensing process, and businesses that understand them are well-positioned to offer outstanding customer experience genuinely. Let’s learn more about this path of demand sensing.
What is demand planning?
A corporation may successfully forecast future demand through demand planning, a supply chain management method, and modify production accordingly. It is a cross-functional approach that assists companies in satisfying consumer demand while reducing excess inventory and preventing supply chain interruptions. Demand planning must be an ongoing procedure thoroughly embedded in a company. This procedure includes reviewing past sales data, consumer patterns, and seasonality information to maximise a company’s capacity to satisfy consumer demand. It also incorporates information from internal and outside sources to predict future demand. The sales and operational plan are then developed using the estimate to satisfy the demand.
Demand sensing techniques are often needed for effective demand planning to forecast demand patterns correctly. This practice has other advantages, such as improved business productivity and customer satisfaction. Profitability, customer happiness, and efficiency improvements can all grow. It aims to create a situation where the supply is successfully lean, and the demand is effectively balanced. It is too difficult to strike the ideal balance between surplus and sufficient, and maintaining that equilibrium is a key problem of demand planning.
Also Read: Top 16 Supply Chain Management Interview Questions & Ans
Importance of demand planning
An efficient supply chain is anchored by demand planning, which performs several crucial tasks:
Every firm is motivated to boost sales and ensure anticipated revenues are realised. However, it might be challenging for shops to keep everything in inventory. Modern consumers take only a short time to form a lasting opinion if a firm fails to satisfy their needs. To prevent stock-outs and be ready for the next sale, demand planning aids in ensuring that businesses have precisely the appropriate amount of goods in the right location.
However, managing sales is only part of it. It also involves developing firms that operate well. By managing inventory space more effectively, demand planning improves corporate efficiency. Selling inventory as rapidly as possible helps firms avoid the risks of overstocking, such as undesired inventory, increased carrying costs, and financial conditions that necessitate offering discounts.
Demand planning is more important than ever since demand is shaped and reshaped by various external factors, including weather conditions, economic trends, and international crises.
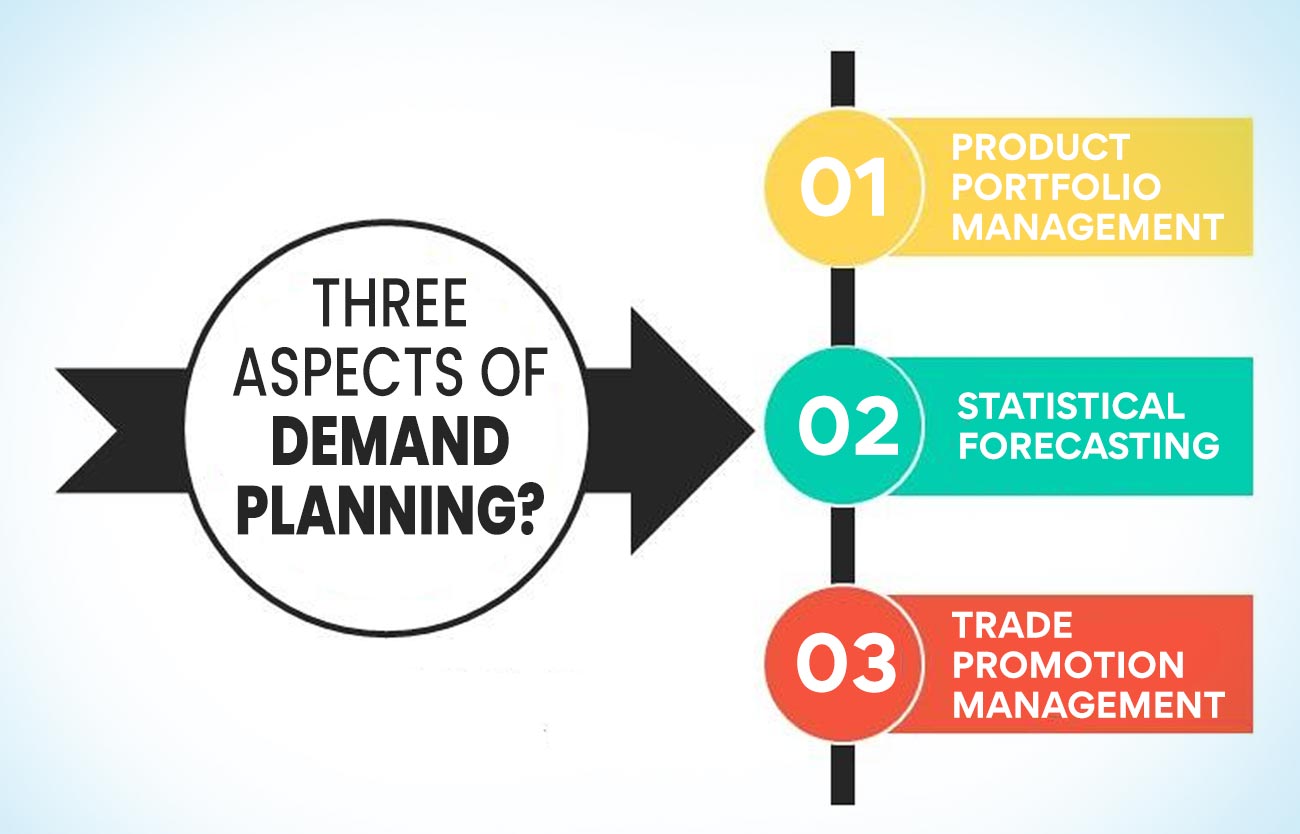
Three aspects of demand planning?
It’s important to keep up with the demand for a product since failing to do so might lead to declining income or even losing consumers. Having the correct quantity of inventory to satisfy customer demand without experiencing shortages or spending money keeping excess inventory is a crucial component of demand planning.
- Product Portfolio Management: This procedure is used to track a product’s lifespan, from the time it is first introduced until the planning of its end of life. Numerous product lines are interdependent; therefore, it’s critical to comprehend how these items affect demand for other products to determine the entire product mix needed to increase market share.
- Statistical forecasting: Using past data and complex statistical techniques, statistical forecasting generates distribution network forecasts. In this area, it’s crucial to assess each model’s precision, spot outliers and exclusions, and comprehend assumptions. Statistical forecasting may also evaluate seasonal fluctuations, such as the spike during festivals.
- Trade Promotion Management: Trade promotions, particularly in retail, impact consumer demand for a product. In the form of freebies, discounts, or promotions, it helps a business engage with a client, and these occasions affect the demand for a product.
Demand Planning vs Demand Forecasting vs Demand Sensing
While we have a thorough understanding of the demand planning idea, let’s explore demand forecasting and demand sensing.
Demand forecasting – It is a step in the bigger demand planning process. Forecast sales entail examining both internal and external data. Forecasts are often made for the next 18 to 24 months; however, the time frame might change based on the product and sector. Businesses routinely modify their estimates as they analyse the most recent data and consider shifting market conditions. Demand prediction becomes the cornerstone of the whole demand planning process as the company determines how it can meet anticipated sales. Demand shaping, or attempting to influence demand through price adjustments, product substitution, promotions, and other strategies, is a component of demand management. Although these phrases are frequently viewed as separate elements of demand management, they are occasionally used interchangeably.
Demand sensing – It is simply the art and science of recognising transient patterns right away to better anticipate what customers want when they want it, and where they want it. Instead of focusing on long-term projections, it emphasises preparation for sudden changes in demand. Even while previous data continues to be a crucial predictor of the future, demand sensing is developing quite quickly. The basis for forecasting is past sales data. For long-term planning, previous sales are useful for estimating future projected levels, but they are less reliable for immediate planning. Demand sensing becomes useful in this situation. Simply put, the most recent past is the best indicator of the very near future if the past is the best predictor of the future. Demand sensing allows firms to question their forecasts using the most recent sales data and make adjustments that increase earnings rather than sticking with the same projection for an entire month.
Demand Sensing: Its Aspects
Demand forecasting uses a high degree of data granularity to examine daily demand variations as closely as possible to the end customer and quickly spot changes in demand patterns. It is increasing supply chain visibility through point-of-sale (PoS), promotion, social media, weather, internet search, and economic data to identify trends that may be used to enhance your forecast and inventory allocation shortly. These demand-sensing features help lessen demand uncertainty and allow for timely prediction revisions.
Demand Sensing: Its Goals
Demand Sensing is a technique and technology that uses precise data on short-term demand to enhance estimates for the near future. This short-term perspective may refer to hours or days depending on how active a company’s supply chain is. Insular thinking has given way to a customer-centric market perspective, asking what consumers want and when. Customers simultaneously want excellent service levels and optimum inventory levels from their distribution networks. Demand sensing is a byproduct of this shift towards interactive supply chains.
Demand sensing’s objective is to assist organisations in making real-time decisions based on current events, not events from a year ago. By assuming that history would repeat itself over a lengthy period, conventional time-series forecasting techniques have latency problems that businesses must solve.
Businesses have since discovered how challenging and time-consuming it is to incorporate real-time data into time-series statistical models. Therefore, it is not unexpected that demand sensing is fundamentally different. It employs various demand signals and unique mathematical algorithms to predict and react to actual occurrences precisely.
Demand Sensing: Its Needs
Businesses in various industries, including those with high sales volumes, have already embraced demand-sensing technologies. Businesses have successfully used this technology to cut down on lead times. Demand sensing technology is likely to bring about a new revolution at a time when supply chain digitisation is a major goal for all businesses.
- Demand latency reduction – Despite having direct access to PoS data, businesses need to leverage it to quickly understand the market and enhance their services. They can separate relevant information from this PoS data using demand sensing, which helps them enhance their sales prediction. After gathering this data, businesses may utilise it to improve their short-term feedback to the production unit and alter the production schedule by accelerating or de-expediting as necessary.
- Calculating the amount of inventory needed to launch a new product – Product life cycles are getting shorter; therefore, businesses must constantly introduce new items that replace their old ones. Demand sensing enables them to fulfil the demand for new items by ensuring they have an adequate supply of their existing products and confidence in their inventory estimates.
- Short-term inventory management improvements – Many brands frequently need help with the problem of excess inventory being kept in the incorrect locations. Demand sensing assists these companies in dynamic inventory optimisation and network balancing by taking into account the inventory currently available in local warehouses and anticipated consumer demand. Businesses can get daily demand data estimates thanks to this, which allows them to manage production capacities, cut stock buildup, and make the supply chain leaner without sacrificing resilience. In the end, this can lower handling and extra manufacturing expenses.
- Close the gap between inbound and outgoing demand – Outbound personnel delivers merchandise to shops and customers, while inbound staff attempts to fill warehouses. These two components are combined by demand sensing, which presents a single worldwide demand picture.
- Improved comprehension of promotion effectiveness – To comprehend the promotional uplift and more accurately predict demand for upcoming promotions, use sell-in statistics, such as promotion qualities, product, and market reports.
- Protecting businesses from seasonal variations – For companies selling seasonal goods of any kind, predicting demand quickly is essential. It gives them the benefit of being quick thinkers or rapid reacters. For instance, a specific business adopting this technology would be the first to learn when all of its rivals ran out of stock. Additionally, they may react swiftly to alter manufacturing and inventories when a product doesn’t sell as anticipated to prevent obsolescence. Expanding the distribution channel’s visibility decreases demand delay and improves supply across the network.
A demand sensing system’s ability to provide fine-grained insight into network-wide inventory and sales helps firms understand what is selling in the market, where it is selling, and how frequently. The functions of the complete planning process, including product creation, category management, trade promotion planning, etc., are optimised by this information. Making the appropriate judgements and being more responsive are the goals of an effective demand-sensing solution. A more agile supply chain reaction requires shorter forecasting lag times. Additionally, with the right professional training, mastering the demand-sensing process with automation and AI technologies is pretty straightforward.
Also Read: What is Supply Chain Finance? A Detailed Analysis
Demand Sensing: Framework
To successfully implement a technology-enabled demand sensing, a business must undergo a few steps to streamline the process. The supply chain can gain better efficiency and accuracy through demand sensing and help earn higher profits. The major task of demand sensing lies towards reducing the time and frame between the occurrence of the event and the reaction given on that event. Companies using demand-sensing techniques are continuously brainstorming to reshape and invent newer techniques to make them more accurate and efficient. A company may detect demand through various methods, and each one should improve reaction times and profit margins. The most substantial returns from demand-sensing activities are largely seen in three domains:
- Projections for the near future using sell-in data – Utilising the most precise historical data at their disposal is one of the finest methods for businesses to begin detecting demand. These companies often analyse their daily sales data over brief periods and adjust the projection. Demand-sensing data is easily available in supply chain planning or enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. Many contemporary planning systems have a built-in short-term statistical forecasting mechanism for more accurate projections in response to evolving demand.
- Include sell-out data – When doing demand sensing, it is important to consider all potential data sources that might enhance the prediction. Customer, point-of-sale, or channel data, for example, can help bridge the gap between the supply chain’s plan and the actual situation by identifying demand trends and providing early warnings of potential problems.
- Include outside data and demand-related causes – Demand sensing must combine demand-related factors to provide a prediction strong enough to react to a wide range of impending circumstances, both known and unknown. These include changes in the stock market, competing for advertising, social media trends, the introduction of new products, the weather, and other outside factors. The complete picture of the need imaginable is produced by combining the sell-in data, sell-out data, and the proper demand factors. The collection of this information serves as a foundation for straight-through demand sensing. As a result, planners might apply their business skills to improve and further anticipate customer services.
Demand Sensing: Limitations
The type of data utilised to understand future wants is the main distinction between demand forecasting and sensing. When preparing for long-term sales, such as future sales, demand forecasting mainly relies on previous data, which is OK but not optimal for short-term planning. Demand sensing, on the other hand, uses cutting-edge technology to predict near-term wants. In a market that prioritises its consumers, the prediction for the near term refers to the dynamic demand-supply chain that satisfies “what the customers want” and “when they want.”
The accuracy of demand sensing forecasts eventually reaches a limit determined by basic restrictions imposed by information theory and the reality that historical data is a poor predictor of supply chain circumstances at any given time. According to information theory, when a model becomes more complex to achieve a “perfect fit,” forecast accuracy eventually suffers. Industry statistics demonstrate that prediction inaccuracy remains a problem even in finely refined models. If available, current demand signals from all points throughout the supply chain must be considered, and new mathematics must be developed to separate the data into predictive and noisy components.
The goal of demand-sensing solutions is to relentlessly shorten the period between events and the responses to those events. More specifically, the aim is to shorten the period between the emergence of a statistically significant mixture of demand signals and the planner’s capacity to respond intelligently to those signals. Traditional demand planning and forecasting are intrinsically unable to accurately predict short-term objectives, particularly when the necessary data is not readily available at the appropriate moment. The largest obstacle to accurate demand-supply forecasting is the need for more data.
The Bottom Line
According to experts, providing the best-in-class supply chain depends on automation and other technological solutions like advanced analytics, artificial intelligence, or sensors. Therefore, businesses will function better than those without when people, processes, and technology are integrated properly. To meet the expectations of the dynamic market, an ideal demand-sensing technology needs a few important statistics, such as demand visibility, demand signal, supply dependability, demand frequency, supply agility, tech investments, and the appropriate strategy. Enrol in an Advanced Executive Certificate in Supply Chain And Operations Management if you want to learn and implement the art of demand sensing in your business. What are you waiting for? Ace your business strategies today!
More Information:
Top Certification Courses In Supply Chain Management For Professionals
Supply Chain Design: What Is It And Why Is It Important?
Difference Between Transportation and Logistics: Key Distinctions!